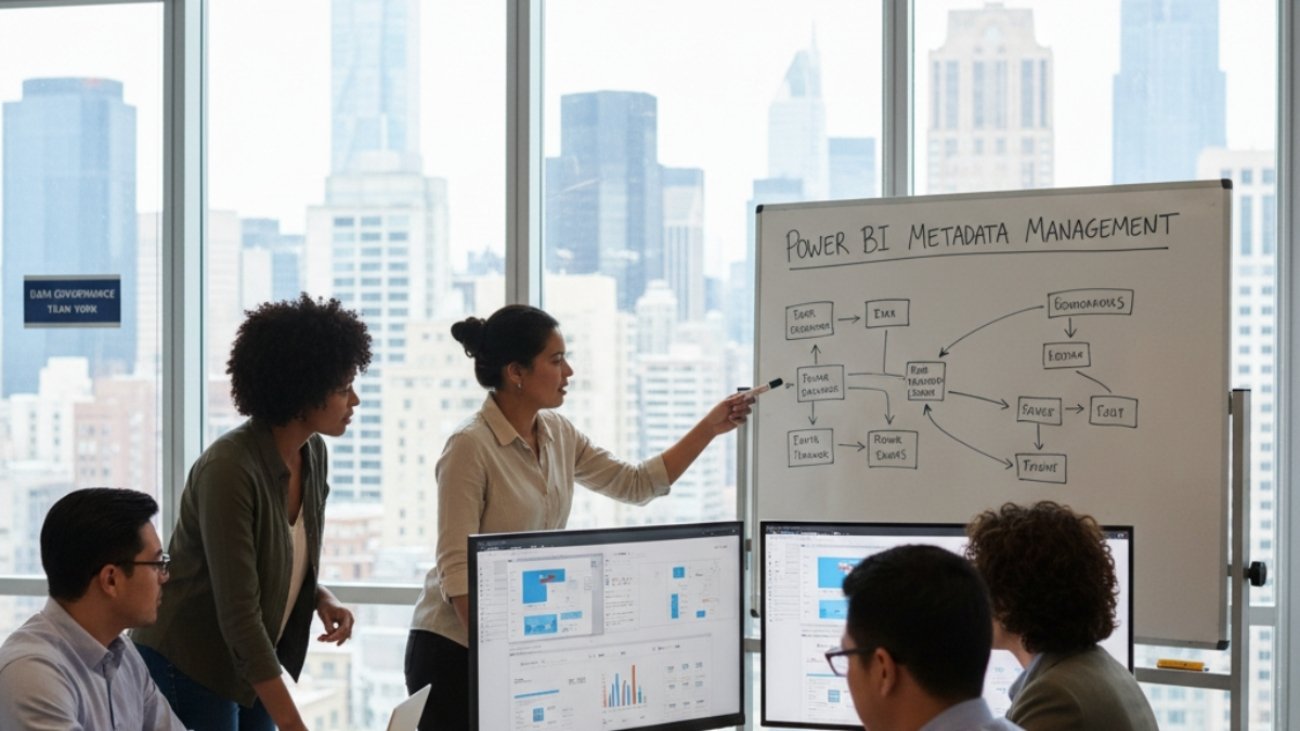
Power BI Metadata Management
Complete Guide to Effective Data Governance and Documentation
📋 Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Power BI Metadata Management
- 2. What is Metadata in Power BI?
- 3. Why Metadata Management Matters
- 4. Types of Metadata in Power BI
- 5. Tools and Techniques for Metadata Management
- 6. Best Practices for Implementation
- 7. Common Challenges and Solutions
- 8. Future of Power BI Metadata Management
🚀 Introduction to Power BI Metadata Management
In today's data-driven business environment, effective metadata management has become the cornerstone of successful Business Intelligence implementations. Power BI metadata management refers to the systematic approach of organizing, documenting, and governing the descriptive information about your data assets within the Power BI ecosystem. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about implementing robust metadata management practices that will transform your Power BI environment from a collection of reports into a well-governed, searchable, and maintainable business intelligence platform.
Metadata management in Power BI extends beyond simple documentation – it encompasses the entire lifecycle of data from source to consumption. When properly implemented, it provides a clear understanding of data lineage, business context, and technical specifications that enable organizations to make informed decisions based on trusted, well-understood data. The importance of this practice cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts data quality, compliance requirements, and the overall return on investment from your Power BI implementation.
Organizations that invest in proper metadata management typically see a 40-60% reduction in time spent on data discovery and troubleshooting, along with significantly improved user adoption rates. This guide will provide you with the frameworks, tools, and best practices necessary to achieve these results in your own Power BI environment, whether you're managing a small departmental implementation or an enterprise-wide deployment across multiple business units.
🎯 Ready to Transform Your Power BI Metadata Management?
📊 What is Metadata in Power BI?
Metadata in Power BI represents the "data about data" – the descriptive information that provides context, meaning, and structure to your business intelligence assets. This includes everything from table and column descriptions to data source information, refresh schedules, user access patterns, and business glossary terms. Understanding the different layers of metadata is crucial for implementing an effective management strategy.
Core Components of Power BI Metadata:
- Technical Metadata: Data types, table relationships, DAX formulas, and connection strings
- Business Metadata: Business definitions, KPI calculations, and contextual descriptions
- Operational Metadata: Refresh history, usage statistics, and performance metrics
- Structural Metadata: Data model hierarchy, security roles, and workspace organization
Technical Metadata Deep Dive
Technical metadata forms the foundation of your Power BI implementation, encompassing all the technical specifications that define how your data is structured and processed. This includes detailed information about data sources, connection parameters, transformation logic applied in Power Query, and the complex web of relationships between different tables in your data model. Understanding and managing this technical metadata is essential for maintaining data integrity and ensuring consistent performance across your reports and dashboards.
The technical metadata layer also includes information about DAX measures, calculated columns, and custom functions that have been implemented across your Power BI environment. This metadata is particularly valuable for impact analysis – understanding which reports and visuals will be affected when changes are made to underlying data structures or business logic. Without proper documentation of technical metadata, organizations often find themselves in situations where seemingly minor changes cascade into unexpected issues across multiple reports and dashboards.
💡 Why Metadata Management Matters
The strategic importance of metadata management extends far beyond simple documentation. In modern business intelligence environments, metadata serves as the bridge between technical implementation and business value, enabling organizations to scale their analytics capabilities while maintaining governance and control. Without effective metadata management, Power BI implementations often struggle with user adoption, data quality issues, and compliance challenges that can significantly undermine the return on investment.
Impact of Metadata Management on BI Success
Business Value Creation
Effective metadata management creates tangible business value through improved decision-making speed and accuracy. When business users can quickly understand the context and reliability of data presented in Power BI reports, they can make decisions with greater confidence and speed. This translates directly to competitive advantages, as organizations can respond more quickly to market changes and opportunities. Studies have shown that companies with mature metadata management practices make decisions 2.5 times faster than their competitors.
The business value extends to risk mitigation as well. Proper metadata management provides the documentation and audit trail necessary for regulatory compliance in industries such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. It also reduces the risk of making decisions based on misunderstood or misinterpreted data, which can have significant financial and strategic implications. Organizations report an average reduction of 40% in data-related decision errors after implementing comprehensive metadata management practices.
🔍 Types of Metadata in Power BI
Understanding the different types of metadata in Power BI is essential for developing a comprehensive management strategy. Each type serves a specific purpose and requires different approaches for capture, maintenance, and governance. The following framework provides a structured way to think about metadata across all aspects of your Power BI implementation.
| Metadata Type | Description | Examples | Primary Users | Management Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descriptive | Human-readable information about data elements | Column descriptions, business glossary terms, data definitions | Business Users | High |
| Structural | Information about data organization and relationships | Table schemas, relationships, hierarchies | Data Modelers | Critical |
| Administrative | Information about data ownership and governance | Data stewards, security classifications, approval workflows | Data Governance Teams | High |
| Operational | Information about data processing and usage | Refresh schedules, usage statistics, performance metrics | IT Operations | Medium |
| Lineage | Information about data flow and transformations | Source-to-target mappings, transformation logic, dependencies | Data Engineers | Critical |
Descriptive Metadata Management
Descriptive metadata is often the most visible type of metadata to end users and plays a crucial role in user adoption and data literacy. This category includes business-friendly descriptions of data elements, glossary terms that define business concepts, and contextual information that helps users understand when and how to use specific data points. The quality and completeness of descriptive metadata directly impacts how quickly new users can become productive with Power BI reports and dashboards.
Managing descriptive metadata effectively requires establishing clear standards for documentation and implementing processes to keep this information current as business requirements evolve. Organizations should consider implementing automated workflows that prompt data stewards to review and update descriptive metadata when underlying data structures change. This proactive approach ensures that the business context remains aligned with the technical implementation, preventing the common scenario where reports become difficult to interpret over time.
🛠️ Tools and Techniques for Metadata Management
The landscape of metadata management tools for Power BI has evolved significantly, offering organizations various options for implementing comprehensive metadata governance. From native Power BI features to specialized third-party solutions, the key is selecting tools that align with your organization's size, technical capabilities, and governance requirements. This section provides a detailed overview of available options and guidance for making the right choice for your environment.
Native Power BI Metadata Features:
- Power BI REST API: Programmatic access to workspace, dataset, and report metadata
- Data Lineage View: Visual representation of data flow between datasets and reports
- Usage Metrics: Built-in analytics for understanding report and dashboard consumption
- Endorsement System: Certification and promotion features for trusted content
- Sensitivity Labels: Classification system for data protection and compliance
Third-Party Metadata Management Solutions
While Power BI's native features provide a solid foundation, many organizations require more comprehensive metadata management capabilities. Third-party solutions offer advanced features such as automated metadata discovery, business glossary management, and integration with broader data governance platforms. These tools typically provide more sophisticated user interfaces for metadata browsing and editing, along with workflow capabilities for maintaining metadata accuracy over time.
Assessment Phase
Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your current metadata landscape. Catalog existing data assets, identify gaps in documentation, and evaluate the technical skills available within your organization. This assessment should also include an inventory of stakeholder requirements across different user groups – from business analysts to data engineers.
Tool Selection
Select metadata management tools based on your assessment findings. Consider factors such as integration capabilities with your existing technology stack, scalability requirements, user experience for different personas, and total cost of ownership. Pilot programs can be valuable for evaluating tools in your specific environment before making final decisions.
Implementation
Implement your chosen solution using a phased approach. Start with critical data assets and gradually expand coverage. Establish clear roles and responsibilities for metadata maintenance, and implement training programs to ensure user adoption. Consider appointing metadata stewards for different business domains to distribute the maintenance workload.
Popular third-party tools in the Power BI ecosystem include Microsoft Purview for enterprise-grade data governance, Collibra for comprehensive data catalog capabilities, and specialized tools like BI Connector and Metadata Manager that focus specifically on Power BI environments. Each tool offers different strengths, and the choice often depends on whether you need a Power BI-specific solution or a broader data governance platform that includes Power BI support.
🚀 Need Help Implementing Metadata Management?
⭐ Best Practices for Implementation
Implementing effective metadata management requires a structured approach that balances technical capabilities with organizational change management. The most successful implementations follow proven best practices that address both the technical and cultural aspects of metadata governance. These practices have been refined through years of enterprise implementations and provide a roadmap for achieving sustainable results.
Organizational Change Management
The technical aspects of metadata management are often easier to address than the organizational changes required for success. Effective metadata management requires cultural changes that emphasize the value of documentation and data governance. Organizations should invest in training programs that help users understand not just how to use metadata tools, but why metadata management is important for their daily work.
Change management should also address the common perception that metadata documentation is "extra work" that slows down project delivery. Successful organizations demonstrate the value of metadata through concrete examples of improved efficiency, reduced errors, and faster onboarding of new team members. They also implement processes that make metadata creation and maintenance as seamless as possible, integrating it into existing development workflows rather than treating it as a separate activity.
Quality Assurance Framework
Establishing a quality assurance framework for metadata ensures that your documentation remains accurate and valuable over time. This framework should include regular audits of metadata completeness, accuracy checks against actual data structures, and validation of business definitions against current organizational understanding. Quality assurance activities should be built into regular development cycles rather than treated as one-time events.
| Quality Dimension | Measurement Criteria | Target Threshold | Review Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Completeness | Percentage of data elements with descriptions | >85% | Monthly |
| Accuracy | Metadata alignment with actual data structures | >95% | Quarterly |
| Currency | Time since last metadata update | <90 days | Ongoing |
| Consistency | Adherence to naming and documentation standards | >90% | Monthly |
⚡ Common Challenges and Solutions
Despite the clear benefits of metadata management, organizations often encounter significant challenges during implementation. Understanding these common obstacles and their proven solutions can help you navigate the implementation process more effectively and avoid costly mistakes. The challenges typically fall into three categories: technical, organizational, and resource-related issues.
Technical Integration Challenges
One of the most frequent technical challenges involves integrating metadata management tools with existing Power BI environments and broader technology ecosystems. Organizations often struggle with data synchronization between different systems, maintaining consistency across multiple data sources, and handling the complexity of modern hybrid cloud architectures. These challenges are compounded when organizations have multiple Power BI tenants or complex security requirements that limit automated metadata discovery.
The solution approach involves careful architecture planning and phased implementation strategies. Organizations should start by mapping their current technical landscape and identifying integration points that are most critical for their use cases. Pilot implementations can help validate integration approaches before committing to enterprise-wide deployments. It's also important to establish clear data flow patterns and error handling procedures to maintain metadata accuracy even when integration points experience issues.
User Adoption and Training
User adoption represents perhaps the greatest challenge in metadata management implementations. Even the most sophisticated technical solution will fail if users don't understand its value or find it too complex to use regularly. Common adoption barriers include lack of training, unclear value proposition, complex user interfaces, and processes that seem to slow down rather than accelerate daily work activities.
Successful adoption strategies focus on demonstrating immediate value to different user groups. For business users, this might involve showing how metadata helps them find relevant reports faster or understand data context more easily. For technical users, the focus might be on how metadata reduces troubleshooting time and improves impact analysis capabilities. Training programs should be role-based and include hands-on exercises that demonstrate real-world scenarios relevant to each user group.
Common Implementation Challenges
Resource and Budget Constraints
Many organizations underestimate the ongoing resource requirements for effective metadata management. While initial implementation requires significant investment in tools and training, the long-term success depends on sustained commitment to metadata maintenance and governance activities. Organizations often struggle to justify the ongoing costs, especially when benefits are not immediately quantifiable or visible to senior leadership.
Addressing resource constraints requires developing a clear business case that demonstrates both quantitative and qualitative benefits. Organizations should track metrics such as time saved on data discovery, reduced errors in reporting, improved compliance readiness, and faster onboarding of new users. Building these metrics into regular business reviews helps maintain executive support and justifies continued investment in metadata management capabilities.
🔮 Future of Power BI Metadata Management
The future of Power BI metadata management is being shaped by advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automated data governance technologies. These emerging capabilities promise to address many of the current challenges around metadata creation, maintenance, and discovery. Understanding these trends can help organizations make strategic decisions about their metadata management investments and prepare for the evolving landscape.
AI-Powered Metadata Discovery
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how organizations discover and catalog metadata. Advanced AI algorithms can now automatically analyze data patterns, identify business entities, and suggest appropriate metadata based on content analysis and usage patterns. These capabilities significantly reduce the manual effort required for initial metadata creation and help maintain accuracy as data structures evolve over time.
Machine learning models are becoming increasingly sophisticated at understanding business context from data usage patterns. They can automatically suggest business-friendly names for technical columns, identify potential data quality issues, and even recommend appropriate visualizations based on data characteristics. This intelligence layer makes metadata management more accessible to business users while reducing the burden on technical teams.
Integration with Modern Data Architectures
The evolution toward modern data architectures, including data mesh and data fabric approaches, is creating new requirements for metadata management. These architectures emphasize distributed data ownership and self-service capabilities, which require more sophisticated metadata governance frameworks. Power BI metadata management solutions are evolving to support these distributed models while maintaining centralized governance and discovery capabilities.
Emerging Trends in Metadata Management:
- Automated Lineage Discovery: AI-powered tools that automatically map data flow across complex architectures
- Natural Language Metadata: Voice and text interfaces for querying and updating metadata
- Real-time Metadata Sync: Instantaneous updates across distributed systems and platforms
- Predictive Data Quality: Machine learning models that predict and prevent data quality issues
- Contextual Recommendations: Personalized metadata suggestions based on user behavior and role
Cloud-Native Governance
The shift toward cloud-native architectures is driving new approaches to metadata management that leverage cloud-specific capabilities such as serverless computing, event-driven architectures, and managed AI services. These approaches enable more scalable and cost-effective metadata management solutions that can adapt to changing business requirements without significant infrastructure investments.
Cloud-native solutions also enable better integration with broader digital transformation initiatives, including customer experience platforms, IoT data streams, and real-time analytics capabilities. This integration creates opportunities for more comprehensive metadata management that spans beyond traditional business intelligence to include all forms of organizational data assets.
Regulatory and Compliance Evolution
Evolving regulatory requirements around data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and AI governance are creating new demands for metadata management capabilities. Organizations need to demonstrate not just what data they have, but how it's being used, who has access to it, and what decisions are being made based on that data. These requirements are driving demand for more sophisticated audit trails and governance workflows within metadata management platforms.
The future regulatory landscape will likely require real-time visibility into data usage patterns, automated compliance reporting, and the ability to quickly respond to data subject requests. Metadata management systems are evolving to provide these capabilities through integration with broader governance, risk, and compliance platforms.
🎯 Conclusion and Next Steps
Effective Power BI metadata management is no longer optional for organizations serious about data-driven decision making. As we've explored throughout this comprehensive guide, the benefits of implementing robust metadata governance extend far beyond simple documentation – they encompass improved user adoption, enhanced data quality, accelerated decision-making, and reduced compliance risks.
The key to success lies in approaching metadata management as a strategic initiative rather than a technical project. This means investing in the right combination of tools, processes, and organizational changes while maintaining focus on delivering tangible business value. Organizations that take a holistic approach to metadata management consistently outperform their peers in terms of analytics maturity and business intelligence ROI.
As you embark on or enhance your metadata management journey, remember that this is an evolutionary process rather than a one-time implementation. Start with the highest-value use cases, demonstrate success, and gradually expand your scope and sophistication. The investment you make today in metadata management will compound over time, creating a foundation for advanced analytics capabilities and sustainable data governance practices.
🚀 Ready to Get Started? Here's Your Action Plan:
- Assess Current State: Conduct a thorough inventory of your existing metadata and identify gaps
- Define Strategy: Establish clear objectives, success metrics, and governance framework
- Select Tools: Choose metadata management tools that align with your requirements and capabilities
- Pilot Implementation: Start with a focused pilot program to validate your approach
- Scale and Optimize: Gradually expand scope while continuously improving processes and user experience
🎯 Transform Your Power BI Environment Today!
Don't let poor metadata management hold back your analytics potential. Our experts are ready to help you implement world-class metadata governance that will transform your Power BI environment.
info@powerbigate.com
Get detailed consultation via email
+1281 631 3767
Speak directly with our experts
Book Free Consultation 30-minute strategy session
📚 Related Resources
Explore these related articles to deepen your Power BI expertise:
Essential Financial KPIs Every Power BI Dashboard Should TrackDiscover the most important financial metrics for executive dashboards and learn how to implement them effectively. Power BI for SaaS Companies: Complete Implementation Guide
Learn how SaaS companies can leverage Power BI for customer analytics, churn prediction, and revenue optimization. Power BI vs Excel for Financial Reporting: Which is Better?
Compare Power BI and Excel for financial reporting needs and understand when to use each tool. How to Build a CFO Executive Dashboard in Power BI + Free Template
Step-by-step guide to creating executive-level financial dashboards with downloadable template. Visit PowerBIGate Homepage
Explore more Power BI resources, tutorials, and expert consulting services.