In the ever-evolving landscape of data analysis and reporting, choosing the right data connection method is crucial for optimizing performance and user experience. Power BI, a leading business analytics tool developed by Microsoft, provides several data connectivity options, with two primary methods standing out: Import Mode and Direct Query Mode. Understanding these options is essential for making informed decisions that align with your analytical needs.
Ultimately, the choice between Import and Direct Query modes should be based on specific analytical requirements, including data volume, update frequency, and performance needs. Understanding these differences empowers users to leverage Power BI’s full potential, ensuring timely and relevant insights for informed decision-making.
Understanding Data Connection Types
Power BI supports a diverse range of data connection types that empower users to connect to various data sources effectively. These connections can be broadly categorized into two main types: Import Mode and Direct Query Mode. Understanding these connection types is vital for optimizing performance, ensuring the timely availability of data, and ultimately enhancing the user experience in your reporting efforts.
Import Mode allows users to bring data into Power BI by creating a local copy of the dataset. This approach is ideal for scenarios where data is relatively static and does not require real-time updates. Once imported, Power BI stores the data in-memory, allowing for rapid access and manipulation. This means users can leverage Power BI’s advanced modeling and transformation capabilities, perform complex calculations, and create rich visualizations without experiencing delays caused by data retrieval. However, it’s essential to regularly refresh the imported data to maintain its accuracy, which can be done through scheduled refreshes. This mode is best suited for smaller datasets or analyses where performance and speed are critical.
In contrast, Direct Query Mode establishes a live connection to the data source, enabling real-time access to data. This method is particularly useful for dynamic business environments where immediate insights are essential. Users can work with larger datasets without the limitations of local storage, and data is always up-to-date since queries are executed directly against the source. However, performance may be affected by network speed, and there may be limitations on data transformations and calculations.
By understanding the differences between Import Mode and Direct Query Mode, Power BI users can make informed decisions about which connection type best suits their analytical needs, ensuring optimal performance and data availability in their reports.
Overview of Import Mode
Import Mode in Power BI is a powerful feature that allows users to pull data into the platform, storing a snapshot of the dataset for analysis. This mode is particularly advantageous when dealing with manageable data volumes that don’t require real-time updates, making it a popular choice for many data analysts and business intelligence professionals. Understanding its key features, advantages, and disadvantages is crucial for optimizing its use in various analytical scenarios.
Key Features of Import Mode
1. Data Storage: When you utilize Import Mode, Power BI creates a snapshot of your data and stores it in its internal storage system. This means that the data is cached, allowing for quicker access during report generation. Since the data is stored in-memory, users can benefit from faster load times when interacting with reports and dashboards.
2. Data Transformations: Import Mode supports extensive data transformation capabilities, enabling users to manipulate the dataset before it is fully loaded into Power BI. This includes filtering, merging, and transforming data from various sources using Power Query, allowing analysts to create a clean, structured dataset that fits their analysis needs.
3. Scheduled Refreshes: Users have the ability to schedule refreshes to update the data at regular intervals. This feature ensures that reports and dashboards reflect the latest available information, even though the data is not real-time. Users can set refresh schedules according to their specific needs, whether it be hourly, daily, or weekly, depending on the frequency of data updates.
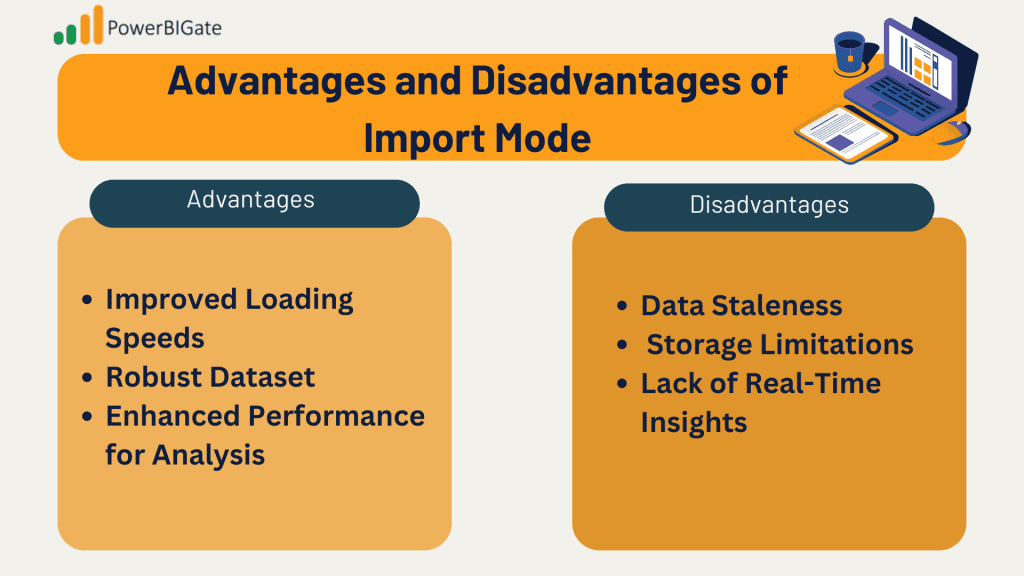
Advantages of Import Mode
· Improved Loading Speeds: One of the most significant benefits of Import Mode is that since data is cached locally, reports load much faster compared to querying data directly from the source. Users can navigate through dashboards and interact with visualizations with minimal delay, providing a better user experience.
· Robust Dataset: Import Mode allows users to create complex data models and perform extensive transformations without impacting real-time performance. This flexibility enables analysts to design intricate relationships between tables, use advanced calculations, and build comprehensive reports without worrying about the performance overhead associated with live queries.
· Enhanced Performance for Analysis: With data pre-loaded into Power BI’s memory, calculations and visualizations are executed quickly. This performance enhancement is particularly beneficial when dealing with large datasets or when complex calculations are required, allowing analysts to derive insights faster.
Disadvantages of Import Mode
· Data Staleness: A notable drawback of Import Mode is that data is not continuously refreshed, which means it may become outdated if the refresh schedule is not adhered to. This limitation can pose challenges in environments where timely data is critical, such as operational dashboards or real-time monitoring.
· Storage Limitations: Power BI imposes storage constraints on datasets, particularly in the Pro version, where the maximum size is currently limited to 1 GB per dataset. For organizations dealing with larger datasets, this limitation can necessitate careful data management and optimization strategies.
· Lack of Real-Time Insights: If up-to-the-minute data is required for decision-making, Import Mode may not be the most suitable choice. While scheduled refreshes can keep data relatively current, they cannot match the immediacy provided by Direct Query Mode, which offers real-time data access.
Import Mode in Power BI is an effective method for users looking to analyze data that doesn’t require constant updates. By understanding its key features, advantages, and disadvantages, users can better leverage this mode to optimize their reporting and analytical workflows. Whether you are creating historical trend analyses or financial reports, Import Mode provides a robust framework for data manipulation and visualization, making it a valuable tool in the Power BI ecosystem. However, for scenarios requiring real-time data, it’s essential to weigh the limitations of Import Mode against the needs of your specific analytical tasks.
Overview of Direct Query Mode
Direct Query Mode in Power BI is a powerful feature designed for users who need real-time access to data stored in external sources. Unlike Import Mode, which stores a static snapshot of data, Direct Query maintains a live connection to the data source. This capability allows queries to run directly on the source at the moment data is required, making it particularly suitable for scenarios where up-to-date information is essential. Understanding the key features, advantages, and disadvantages of Direct Query Mode is vital for users who want to leverage its full potential effectively.
Key Features of Direct Query Mode
1. Real-Time Data Access: One of the standout features of Direct Query Mode is its ability to retrieve data live from the source. This means users can access the most current information without needing to wait for scheduled refreshes. For organizations that rely on dynamic data environments, this functionality is crucial, enabling them to make informed decisions based on the latest metrics and insights.
2. Limited Data Transformations: While Direct Query Mode allows for some data transformations, its capabilities are more restricted compared to Import Mode. Since transformations need to be managed within the source database, users may find themselves limited to simpler calculations and manipulations. This necessitates a deeper understanding of the data structure and the ability to perform complex transformations directly within the source database.
3. Dependency on Source Performance: The performance of queries executed in Direct Query Mode is contingent upon the speed and performance of the underlying data source. If the source database is slow or encounters performance issues, these problems will directly impact the responsiveness of reports and dashboards in Power BI. Users must ensure that their data sources are optimized for best performance to avoid bottlenecks.
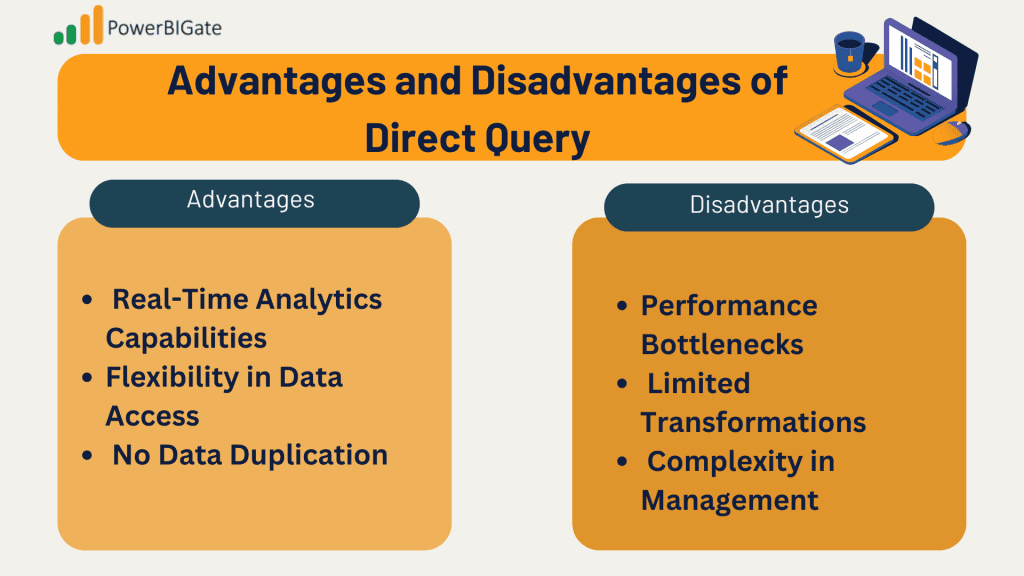

Advantages of Direct Query
· Real-Time Analytics Capabilities: One of the primary advantages of Direct Query Mode is its ability to provide real-time analytics. This feature is particularly valuable for dashboards that track metrics such as sales performance, website traffic, or operational data. Organizations can gain insights immediately, which is essential for timely decision-making.
· Flexibility in Data Access: Direct Query allows users to pull from large datasets without the constraints of local storage, making it suitable for organizations with extensive databases. Users are not limited by the storage capacities of Power BI, allowing them to query data across multiple tables and sources seamlessly.
· No Data Duplication: Since data is queried directly from the source, there is no need for data duplication within Power BI. This not only reduces the risk of data inconsistency but also simplifies the management of data sources, as users always work with the most current information available.
Disadvantages of Direct Query
· Performance Bottlenecks: Despite its advantages, Direct Query can suffer from performance bottlenecks. Network latency or the speed of the source system can lead to delays in data retrieval, which may frustrate users expecting instantaneous responses. Organizations need to be cautious about the performance of their data sources and network infrastructure to mitigate these risks.
· Limited Transformations: Users often find themselves restricted to simpler calculations and transformations when using Direct Query. This limitation requires a solid understanding of the data source’s capabilities and may necessitate additional effort to prepare data for analysis. Users may need to rely more on the source database for complex data manipulations, which can complicate the analytical process.
· Complexity in Management: Managing and optimizing queries in Direct Query Mode can be more complex than in Import Mode. Users need to possess a good understanding of SQL and the underlying data source’s structure to efficiently query and manipulate the data. This complexity may pose challenges for less technical users who may struggle with the intricacies of SQL and database management.
Direct Query Mode in Power BI is a powerful tool for organizations that require real-time data access and flexibility in working with large datasets. However, it comes with its own set of challenges, including potential performance issues, limitations in transformation capabilities, and increased complexity in management. Understanding these factors is crucial for effectively leveraging Direct Query in your analytical workflows. By weighing the advantages and disadvantages, users can make informed decisions about when to utilize Direct Query Mode, ensuring they maximize the potential of Power BI while meeting their specific data needs.
Key Differences Between Import and Direct Query
When deciding between Import Mode and Direct Query Mode, it’s essential to consider several fundamental differences:
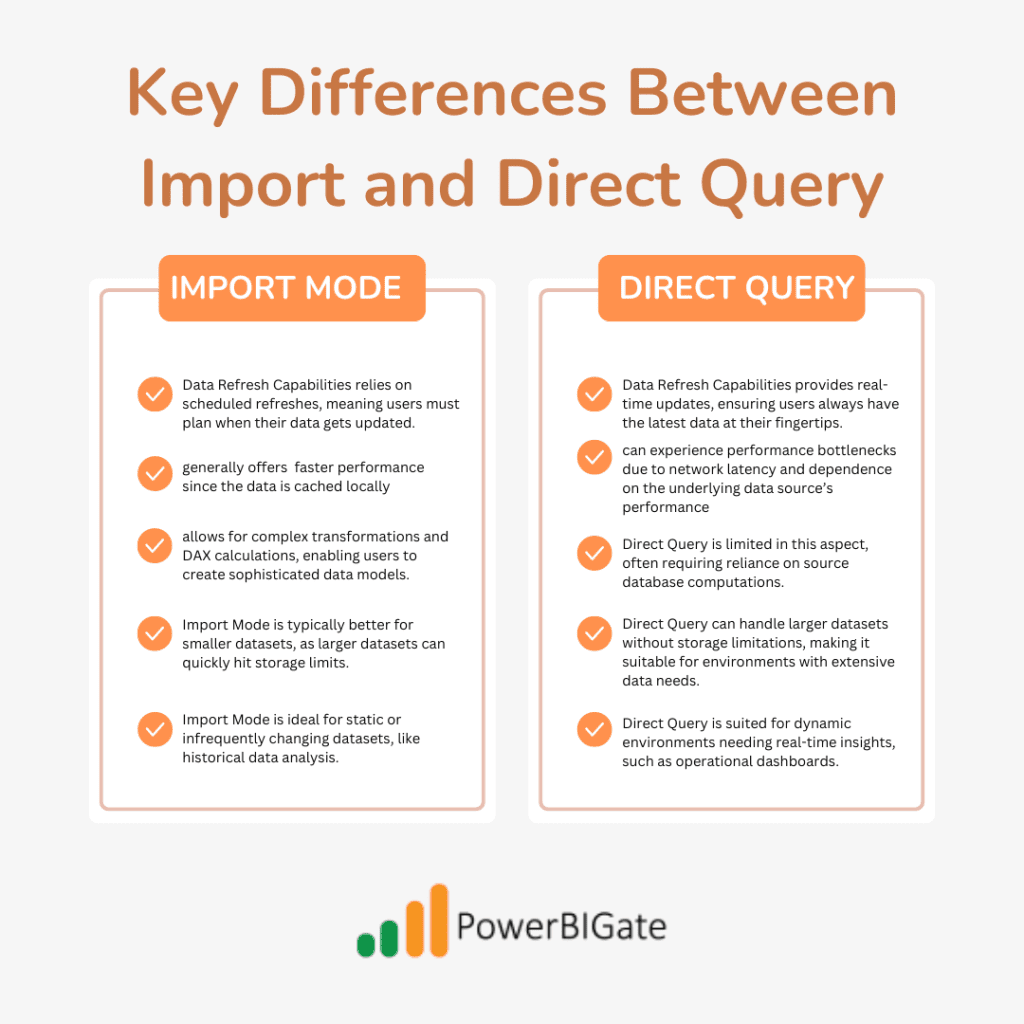
- Data Refresh Capabilities:
- Import Mode relies on scheduled refreshes, meaning users must plan when their data gets updated.
- Direct Query provides real-time updates, ensuring users always have the latest data at their fingertips.
- Performance and Speed:
- Import Mode generally offers faster performance since the data is cached locally.
- Direct Query can experience performance bottlenecks due to network latency and dependence on the underlying data source’s performance.
- Data Transformation:
- Import Mode allows for complex transformations and DAX calculations, enabling users to create sophisticated data models.
- Direct Query is limited in this aspect, often requiring reliance on source database computations.
- Data Volume Handling:
- Import Mode is typically better for smaller datasets, as larger datasets can quickly hit storage limits.
- Direct Query can handle larger datasets without storage limitations, making it suitable for environments with extensive data needs.
- Use Cases:
- Import Mode is ideal for static or infrequently changing datasets, like historical data analysis.
- Direct Query is suited for dynamic environments needing real-time insights, such as operational dashboards.

When to Use Import Mode
Import Mode is ideal for scenarios where:
- Data is relatively static and does not change frequently.
- Smaller datasets (less than 1 GB) are being analyzed, allowing for quick transformations and report loading.
- Complex calculations and optimizations are necessary, benefitting from pre-loaded data.
Examples:
- Financial Reporting: Organizations can use Import Mode for monthly or quarterly financial reports where real-time updates are not critical.
- Historical Trend Analysis: Analysts may want to evaluate past data trends without needing current updates.
When to Use Direct Query Mode
Direct Query should be utilized in situations requiring:
- Real-time analytics where immediate insights from live data are necessary.
- Large datasets that are continuously updated, such as operational dashboards or real-time monitoring systems.
Examples:
- Operational Dashboards: Companies may require live updates on metrics like sales, inventory levels, or customer interactions to make timely decisions.
- Dynamic Reporting: Scenarios where business conditions change rapidly necessitate real-time data access for informed decision-making.
Conclusion
Deciding between Import and Direct Query modes in Power BI is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of your business analysis tasks. Each method has distinct advantages and limitations tailored to different analytical needs, which can significantly impact performance, data accessibility, and overall user experience.
Import Mode is often the preferred choice when working with relatively static datasets. It allows users to load data into Power BI, storing a snapshot that enables fast report generation and complex data transformations. This method is beneficial for scenarios where historical data is analyzed, such as financial reporting and trend analysis, where real-time data is not essential. However, the primary drawback is the reliance on scheduled refreshes to keep the data current, which can lead to outdated insights if not managed properly.
Conversely, Direct Query Mode is ideal for environments requiring real-time data access. By maintaining a live connection to the data source, this method ensures that users can retrieve the most up-to-date information on demand, making it suitable for operational dashboards and dynamic reporting. However, it has limitations in terms of data transformations and can be affected by network performance issues.
As Power BI continues to evolve and adapt to the changing landscape of data analytics, understanding these connectivity modes becomes increasingly important. Users need to consider their specific analytical requirements, such as data volume, update frequency, and performance needs. By making informed decisions about which connection method to use, organizations can leverage Power BI’s capabilities more effectively, ensuring their data-driven insights are timely, relevant, and actionable. Ultimately, the right choice between Import and Direct Query can enhance decision-making processes and drive business success.
Final Thoughts: When assessing your analytical needs, consider factors like data volume, freshness requirements, and performance demands. By choosing the right data connection method, you can maximize your Power BI experience and ensure that your data-driven insights are timely, relevant, and actionable.
What has been your experience with using Import or Direct Query in Power BI, and how has it influenced your data analysis outcomes? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
