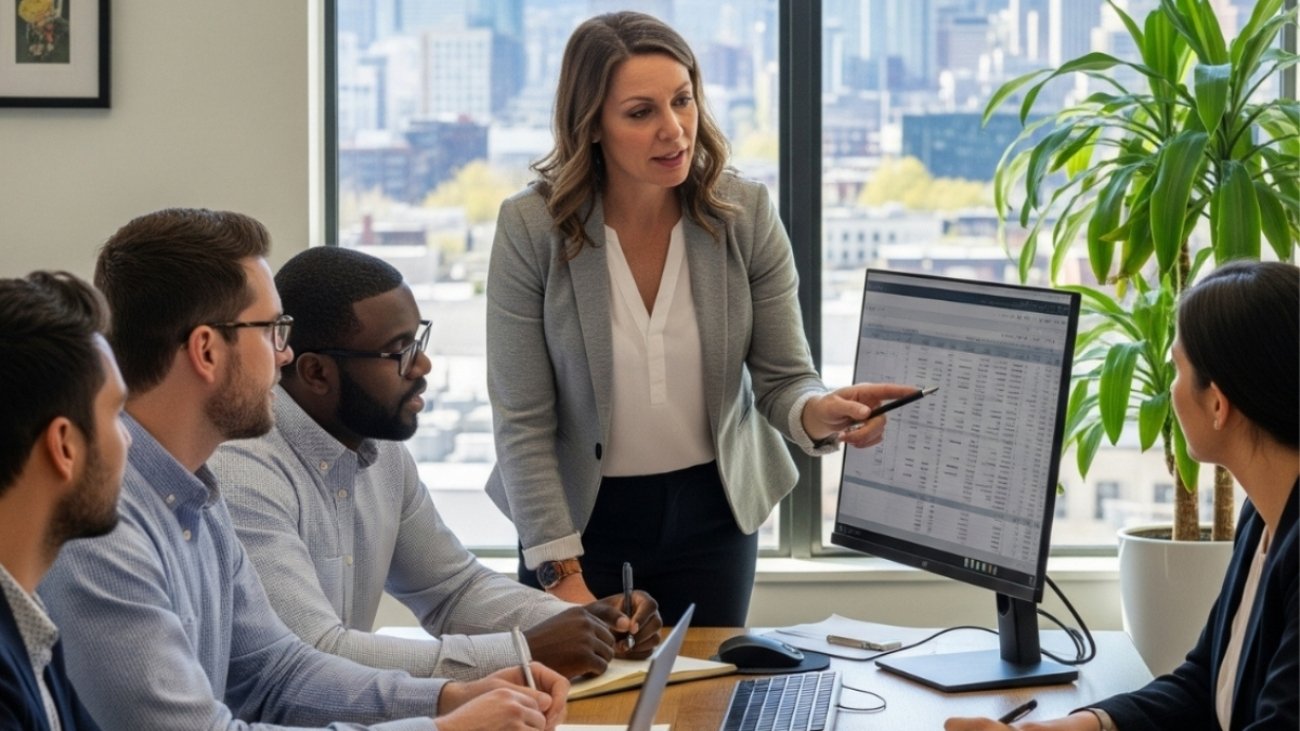
Power BI vs Excel for Financial Reporting: Why It's Time to Upgrade
The Evolution of Financial Reporting Tools
Financial reporting has undergone a dramatic transformation in the digital age. Traditional spreadsheet-based reporting, primarily through Microsoft Excel, dominated the landscape for over three decades. However, the increasing complexity of business data, the need for real-time insights, and the demand for interactive visualizations have created a paradigm shift toward modern business intelligence tools like Power BI.
The transition from static Excel spreadsheets to dynamic Power BI dashboards represents more than just a technological upgrade—it's a fundamental change in how organizations approach financial analysis, data visualization, and strategic decision-making. Understanding the nuances of Power BI vs Excel dashboards is crucial for finance professionals, CFOs, and business leaders who want to stay competitive in today's data-driven economy.
This comprehensive analysis will explore every aspect of both platforms, from basic functionality to advanced analytics capabilities, helping you make an informed decision about whether it's time to upgrade your financial reporting infrastructure. We'll examine real-world scenarios, cost implications, implementation strategies, and long-term benefits to provide you with actionable insights for your organization's digital transformation journey.
Ready to Transform Your Financial Reporting?
Our Power BI experts can help you migrate from Excel to modern dashboards that deliver real-time insights and drive better business decisions.
Understanding Excel's Role in Financial Reporting
Microsoft Excel has been the undisputed champion of financial reporting for generations of finance professionals. Its flexibility, ubiquity, and familiar interface have made it the go-to tool for everything from simple budgeting exercises to complex financial models. Excel's strength lies in its versatility—it can function as a database, calculator, chart generator, and report builder all in one application.
However, as businesses have grown more complex and data sources have multiplied, Excel's limitations have become increasingly apparent. While Excel excels at handling structured data and performing calculations, it struggles with large datasets, real-time data integration, and collaborative workflows. The manual nature of Excel-based reporting processes often leads to version control issues, data integrity problems, and significant time investments in routine tasks.
Excel's Traditional Strengths
- Universal familiarity and ease of use
- Flexible data manipulation capabilities
- Advanced formula and calculation functions
- Offline accessibility and portability
- Cost-effective for small-scale operations
Excel's Growing Limitations
- Manual data entry and update processes
- Limited real-time collaboration features
- Scalability issues with large datasets
- Version control and data integrity challenges
- Static reporting with limited interactivity
Power BI: The Modern Business Intelligence Solution
Power BI represents Microsoft's answer to the evolving needs of modern businesses. Designed from the ground up as a business intelligence platform, Power BI addresses many of the limitations that financial professionals encounter when relying solely on Excel for reporting and analysis. The platform combines data visualization, analytics, and business intelligence capabilities in a unified, cloud-based solution.
What sets Power BI apart in the Power BI vs Excel dashboards comparison is its ability to connect to multiple data sources simultaneously, transform raw data into meaningful insights, and present information through interactive visualizations that update in real-time. This capability is particularly valuable for financial reporting, where timely access to accurate data can significantly impact decision-making processes.
Power BI's strength lies not in replacing Excel entirely, but in complementing it by handling the heavy lifting of data processing, visualization, and distribution while allowing Excel to continue serving its role in detailed analysis and modeling. This symbiotic relationship creates a powerful ecosystem for comprehensive financial reporting and analysis.
Detailed Comparison: Power BI vs Excel Dashboards
| Feature | Excel | Power BI | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Connectivity | Limited native connectors, manual imports | 200+ data connectors, automatic refresh | Power BI |
| Real-time Updates | Manual refresh required | Automatic, scheduled, and streaming refresh | Power BI |
| Data Volume Handling | 1M rows limit, performance degrades | Billions of rows, optimized performance | Power BI |
| Collaboration | Email sharing, version conflicts | Cloud sharing, real-time collaboration | Power BI |
| Visualization Options | Basic charts, limited customization | Interactive visuals, custom visuals marketplace | Power BI |
| Mobile Access | Limited mobile functionality | Native mobile apps, responsive design | Power BI |
| Learning Curve | Familiar to most users | Requires training and adaptation | Excel |
| Cost | Included in Office suite | Additional subscription required | Excel |
| Advanced Analytics | Basic statistical functions | AI insights, predictive analytics, DAX | Power BI |
| Security | File-level security | Row-level security, enterprise governance | Power BI |
Performance and Scalability Analysis
Performance Comparison: Handling Large Financial Datasets
60% Efficiency
90% Efficiency
Based on processing 1M+ financial records with multiple data sources
When examining performance metrics in the Power BI vs Excel dashboards comparison, the differences become stark as data complexity and volume increase. Excel's architecture, originally designed for smaller datasets and simpler calculations, begins to show significant performance degradation when handling the large, multi-source datasets common in modern financial reporting.
Data Processing Capabilities
Excel's row limitation of approximately 1.048 million rows per worksheet may seem adequate for many financial reports, but this constraint becomes problematic when dealing with detailed transaction data, multi-year historical analysis, or consolidated reporting across multiple entities. Power BI's ability to handle billions of rows while maintaining responsive performance makes it ideal for enterprise-level financial reporting requirements.
The data transformation capabilities also differ significantly between the two platforms. Excel's Power Query provides basic data transformation features, but Power BI's enhanced version offers more sophisticated data modeling capabilities, including advanced DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) functions that enable complex financial calculations and KPI development.
Real-time Data Integration and Automation
One of the most compelling advantages in the Power BI vs Excel dashboards debate is the approach to data integration and automation. Excel's reliance on manual data imports and updates creates bottlenecks in the reporting process and increases the risk of working with outdated information—a critical concern in financial reporting where timing can significantly impact decision-making.
Power BI's automated data refresh capabilities transform the reporting workflow from a reactive, manual process to a proactive, automated system. Financial reports can be configured to update hourly, daily, or in real-time, ensuring that stakeholders always have access to the most current financial information. This automation extends beyond simple data updates to include the recalculation of KPIs, variance analysis, and trend identification.
💡 Key Insight
Organizations typically reduce their financial reporting time by 70-80% when transitioning from Excel-based to Power BI-based reporting systems, while simultaneously improving data accuracy and stakeholder satisfaction.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Financial Teams
The financial implications of choosing between Power BI vs Excel dashboards extend far beyond the initial licensing costs. While Excel may appear more cost-effective due to its inclusion in Microsoft Office suites, a comprehensive total cost of ownership analysis reveals a more complex picture that favors Power BI for organizations with substantial financial reporting requirements.
Direct Costs Comparison
| Cost Factor | Excel (Annual) | Power BI Pro (Annual) | Power BI Premium (Annual) |
|---|---|---|---|
| License Cost per User | $70-$150 | $120 | $240 |
| Infrastructure Costs | Minimal | Cloud-based | Cloud-based |
| Training Requirements | Low | Medium | Medium-High |
| Maintenance Overhead | High (manual) | Low (automated) | Low (automated) |
Hidden Costs and Efficiency Gains
The hidden costs associated with Excel-based financial reporting often dwarf the apparent savings from lower licensing fees. These include the time invested in manual data compilation, the risk of errors requiring correction and restatement, the opportunity cost of delayed reporting, and the limitation on analytical depth due to performance constraints.
Power BI's automation capabilities translate into significant labor cost savings. Financial analysts can redirect their time from routine data compilation tasks to higher-value analysis and strategic insights. The platform's self-service capabilities also reduce the burden on IT departments for report creation and maintenance.
Implementation Strategy and Migration Planning
Power BI Migration Roadmap for Financial Teams
Assessment Phase (2-4 weeks)
Inventory existing Excel reports, identify data sources, assess user requirements, and establish success metrics for the migration process.
Infrastructure Setup (1-2 weeks)
Configure Power BI workspace, establish data gateways, set up security protocols, and create user accounts and permissions structure.
Pilot Implementation (4-6 weeks)
Migrate 2-3 critical financial reports, train key users, gather feedback, and refine processes based on initial experience.
Full Deployment (8-12 weeks)
Migrate remaining reports, provide comprehensive user training, establish governance protocols, and implement change management procedures.
Optimization Phase (Ongoing)
Monitor performance, gather user feedback, implement advanced features, and continuously improve dashboard effectiveness and user adoption.
Advanced Analytics and AI Capabilities
The integration of artificial intelligence and advanced analytics represents one of the most significant advantages in the Power BI vs Excel dashboards comparison. While Excel offers basic statistical functions and limited forecasting capabilities, Power BI incorporates machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and predictive analytics that can transform raw financial data into actionable insights.
Power BI's AI features include automatic anomaly detection, which can identify unusual patterns in financial data that might indicate errors, fraud, or emerging trends. The platform's Q&A feature allows users to ask questions in natural language and receive immediate visual answers, democratizing data access for non-technical stakeholders.
Key AI-Powered Features for Financial Reporting
🔍 Smart Insights
Automatically identifies trends, outliers, and patterns in financial data without manual analysis.
📈 Predictive Analytics
Forecasts future financial performance based on historical data and external factors.
🗣️ Natural Language Q&A
Allows stakeholders to ask questions about financial data using everyday language.
🚨 Anomaly Detection
Automatically flags unusual patterns that may require investigation or immediate attention.
Security and Governance Considerations
Financial data security is paramount in any reporting solution, and the Power BI vs Excel dashboards comparison reveals significant differences in security architecture and governance capabilities. Excel's file-based security model, while familiar and straightforward, lacks the sophisticated access controls and audit trails required for enterprise financial reporting.
Power BI's enterprise-grade security features include row-level security (RLS), which allows organizations to restrict data access based on user roles and responsibilities. This capability is particularly valuable in financial reporting, where different stakeholders should have access to different levels of financial detail and different organizational segments.
Security Feature Comparison
✅ Power BI Security Advantages
- Row-level security and dynamic filtering
- Azure Active Directory integration
- Comprehensive audit logs and monitoring
- Data loss prevention (DLP) policies
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Multi-factor authentication support
⚠️ Excel Security Limitations
- File-level security only
- Limited audit trail capabilities
- Manual access control management
- Vulnerability to email-based sharing
- No centralized governance
- Version control challenges
User Experience and Collaboration
The user experience differential in Power BI vs Excel dashboards extends beyond individual productivity to encompass organizational collaboration and knowledge sharing. Excel's traditional approach to collaboration—sharing files via email or network drives—creates silos and version conflicts that can compromise data integrity and decision-making speed.
Power BI's cloud-based collaboration model enables real-time sharing and collaborative analysis. Multiple users can simultaneously view and interact with reports, while commenting and annotation features facilitate discussion and decision-making directly within the reporting environment. This collaborative approach transforms financial reporting from a periodic, batch-driven process to a continuous, interactive dialogue.
Mobile and Remote Access Capabilities
The increasing demand for mobile access to financial data has become a critical factor in the Power BI vs Excel dashboards decision. Excel's mobile applications, while functional, provide limited interactivity and poor optimization for financial dashboard viewing on smaller screens.
Power BI's native mobile applications are specifically designed for dashboard consumption, providing full interactivity, touch-optimized navigation, and offline capabilities. This mobile-first approach ensures that financial stakeholders can access critical information regardless of their location or device, supporting the distributed and remote work environments that have become increasingly common.
Industry-Specific Financial Reporting Requirements
Different industries have unique financial reporting requirements that influence the Power BI vs Excel dashboards decision. Healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA regulations while tracking patient care costs and revenue cycles. Manufacturing companies require detailed cost accounting and production efficiency metrics. Financial services firms need regulatory compliance reporting and risk management dashboards.
Power BI's industry-specific templates and pre-built connectors address these varied requirements more effectively than Excel's generic approach. The platform includes specialized visuals for financial services risk analysis, healthcare patient flow tracking, retail inventory management, and manufacturing performance monitoring. These industry-focused capabilities reduce implementation time and ensure compliance with sector-specific reporting standards.
Industry-Specific Advantages
| Industry | Excel Limitations | Power BI Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Manual HIPAA compliance tracking | Built-in compliance features, patient privacy controls |
| Financial Services | Limited regulatory reporting capabilities | Regulatory templates, risk analytics, stress testing |
| Manufacturing | Static production cost analysis | Real-time production monitoring, IoT integration |
| Retail | Manual inventory reconciliation | Dynamic inventory tracking, sales forecasting |
| Non-profit | Basic fund accounting | Grant tracking, donor analytics, impact reporting |
Training and Change Management
Successfully transitioning from Excel to Power BI requires comprehensive change management and training programs. While Excel's familiarity reduces initial resistance, organizations must invest in user education to maximize Power BI's capabilities. The learning curve for Power BI varies depending on user roles—executives may only need dashboard consumption training, while financial analysts require comprehensive data modeling and DAX formula education.
Effective training programs should include hands-on workshops, role-specific curricula, and ongoing support resources. Organizations that invest in comprehensive training see significantly higher adoption rates and faster realization of Power BI's benefits. The key is to demonstrate how Power BI enhances rather than replaces existing Excel skills, showing users how the platforms work together in an integrated analytics ecosystem.
👥 Executive Training Focus
- Dashboard navigation and interpretation
- Mobile app usage and alerts
- Collaborative features and commenting
- Understanding drill-through capabilities
📊 Analyst Training Focus
- Data modeling and relationships
- DAX formulas and calculated measures
- Advanced visualizations and custom visuals
- Performance optimization techniques
Integration with Existing Financial Systems
The ability to integrate with existing financial systems is crucial in the Power BI vs Excel dashboards evaluation. Most organizations have invested heavily in ERP systems, accounting software, and specialized financial applications. Excel's integration capabilities are primarily limited to manual imports and basic API connections, requiring significant manual intervention to maintain data currency.
Power BI's extensive connector library includes direct integrations with major ERP systems like SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics, as well as cloud-based financial platforms like Salesforce, QuickBooks, and NetSuite. These native connectors enable automated data refresh and real-time reporting without requiring complex ETL processes or IT intervention.
Common Financial System Integrations
- ERP Systems: SAP, Oracle EBS, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Sage
- Accounting Software: QuickBooks, Xero, NetSuite, Sage Intacct
- CRM Platforms: Salesforce, HubSpot, Microsoft Dynamics CRM
- Banking Systems: Direct bank feeds, treasury management systems
- Expense Management: Concur, Expensify, Chrome River
- Budgeting Tools: Adaptive Insights, Anaplan, Prophix
ROI Measurement and Success Metrics
Measuring the return on investment for Power BI implementation requires establishing clear metrics that go beyond simple cost comparisons. Organizations typically see ROI through reduced report preparation time, improved decision-making speed, enhanced data accuracy, and increased stakeholder satisfaction with financial reporting.
📈 Typical ROI Metrics for Power BI Implementation
Time Savings: 60-80% reduction in report preparation time
Data Accuracy: 95%+ reduction in manual data entry errors
Decision Speed: 50% faster financial analysis and reporting cycles
User Satisfaction: 85%+ stakeholder satisfaction with enhanced reporting capabilities
Future-Proofing Your Financial Reporting Infrastructure
The Power BI vs Excel dashboards decision should consider long-term technology trends and organizational growth. Excel's architecture, while continuously improved, remains fundamentally designed for individual productivity rather than enterprise-scale data analytics. Power BI's cloud-native architecture and continuous feature updates position it better for future analytical requirements.
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced predictive analytics are being integrated into Power BI at an accelerated pace. Organizations that establish Power BI-based reporting infrastructure today will be better positioned to leverage these advanced capabilities as they become available, while Excel-based organizations may face more complex migration challenges in the future.
Best Practices for Hybrid Environments
Many organizations find that a hybrid approach, leveraging both Excel and Power BI strengths, provides the optimal solution. Excel continues to excel at detailed financial modeling, ad-hoc analysis, and complex calculations, while Power BI handles data visualization, automated reporting, and stakeholder communication.
Recommended Hybrid Architecture
📊 Use Excel For:
- Complex financial modeling and scenarios
- Detailed variance analysis and calculations
- Ad-hoc data analysis and exploration
- Budget preparation and planning workflows
- Individual analyst productivity tasks
⚡ Use Power BI For:
- Executive dashboards and KPI monitoring
- Automated monthly/quarterly reporting
- Multi-source data integration and visualization
- Stakeholder self-service analytics
- Real-time performance monitoring
Common Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Organizations transitioning from Excel to Power BI often encounter predictable challenges that can be mitigated with proper planning. Data quality issues, user resistance, and governance concerns are among the most common obstacles to successful implementation.
Data quality problems in Excel-based systems become more apparent when migrating to Power BI's automated environment. Inconsistent naming conventions, manual data entry errors, and fragmented data sources must be addressed during the migration process. Establishing data governance protocols and quality assurance procedures is essential for successful Power BI implementation.
Common Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Data Quality Issues
Solution: Implement data validation rules, establish standardized naming conventions, and create automated data quality checks within Power BI data flows.
User Resistance
Solution: Provide comprehensive training, demonstrate immediate value through pilot projects, and establish change champions within each department.
Security and Governance
Solution: Establish clear data governance policies, implement role-based access controls, and create audit procedures for data access and usage.
Technical Integration
Solution: Work with IT teams to establish proper data gateways, configure refresh schedules, and ensure adequate bandwidth for data synchronization.
🚀 Ready to Upgrade Your Financial Reporting?
Transform your organization's financial analysis capabilities with our expert Power BI implementation services. Our certified consultants will guide you through every step of the migration process, from initial assessment to full deployment and user training.
Conclusion: Making the Strategic Decision
The Power BI vs Excel dashboards comparison reveals that while both tools have their place in modern financial reporting, Power BI represents the future of business intelligence and data visualization. Excel's continued relevance lies in its strength for detailed analysis and financial modeling, but Power BI's superior capabilities in data integration, visualization, collaboration, and automation make it the clear choice for organizational reporting and stakeholder communication.
The decision to upgrade from Excel to Power BI should be based on your organization's specific needs, data complexity, user requirements, and strategic objectives. Small organizations with simple reporting needs may continue to find Excel adequate, while larger enterprises with complex data environments and sophisticated analytical requirements will benefit significantly from Power BI's advanced capabilities.
The most successful organizations adopt a strategic approach that leverages both platforms' strengths while gradually transitioning routine reporting functions to Power BI. This hybrid strategy minimizes disruption while maximizing the benefits of modern business intelligence capabilities. As data complexity continues to grow and stakeholder expectations for real-time insights increase, the migration from Excel-based to Power BI-based financial reporting becomes not just advantageous but essential for competitive success.
The investment in Power BI training, implementation, and change management pays dividends through improved decision-making speed, enhanced data accuracy, and increased organizational agility. Organizations that make this transition proactively position themselves for future growth and analytical sophistication, while those that delay risk falling behind in an increasingly data-driven business environment.
📚 Related Resources
Explore these additional resources to enhance your Power BI knowledge and financial reporting capabilities:
🏠 PowerBI Gate Homepage - Your Complete Power BI Resource Center 📊 Essential Financial KPIs Every Power BI Dashboard Should Track 💼 Power BI for SaaS Companies: Complete Implementation Guide 👨💼 How to Build a CFO Executive Dashboard in Power BI (Free Template)🎯 Key Takeaways
Power BI vs Excel dashboards: Power BI wins for automation, scalability, and collaboration, while Excel remains valuable for detailed analysis. The future belongs to integrated environments that leverage both platforms strategically for maximum financial reporting effectiveness.