Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, the security of information is of utmost importance, especially when it comes to sensitive business data. As organizations increasingly rely on powerful analytics tools like Power BI to gain insights and make informed decisions, ensuring the security of their data and reports becomes critical. Proper security measures in Power BI not only protect an organization’s confidential information but also maintain data integrity and privacy.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of Power BI security, exploring the various features, best practices, and strategies that can be employed to safeguard your data and reports. By the end, you should have a clear understanding of how to protect your valuable assets and ensure a secure Power BI environment.
Understanding Power BI Security Features
Before diving into best practices, let’s familiarize ourselves with the security features Power BI offers. Power BI provides a robust set of tools to secure your data at different levels, ensuring a comprehensive security framework.
Data Encryption
Power BI ensures that data is secure during transit and at rest. It employs industry-standard encryption protocols to safeguard sensitive information. Data encryption is applied when data is imported into Power BI, while in storage, and during transmission to the Power BI service. This protects data from unauthorized access, ensuring confidentiality.
User Authentication and Single Sign-On
Power BI integrates seamlessly with Azure Active Directory (AAD), Microsoft’s identity and access management solution. AAD provides robust user authentication, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access your Power BI environment. Single Sign-On (SSO) enhances security and user experience, allowing users to access all authorized resources with a single set of credentials.
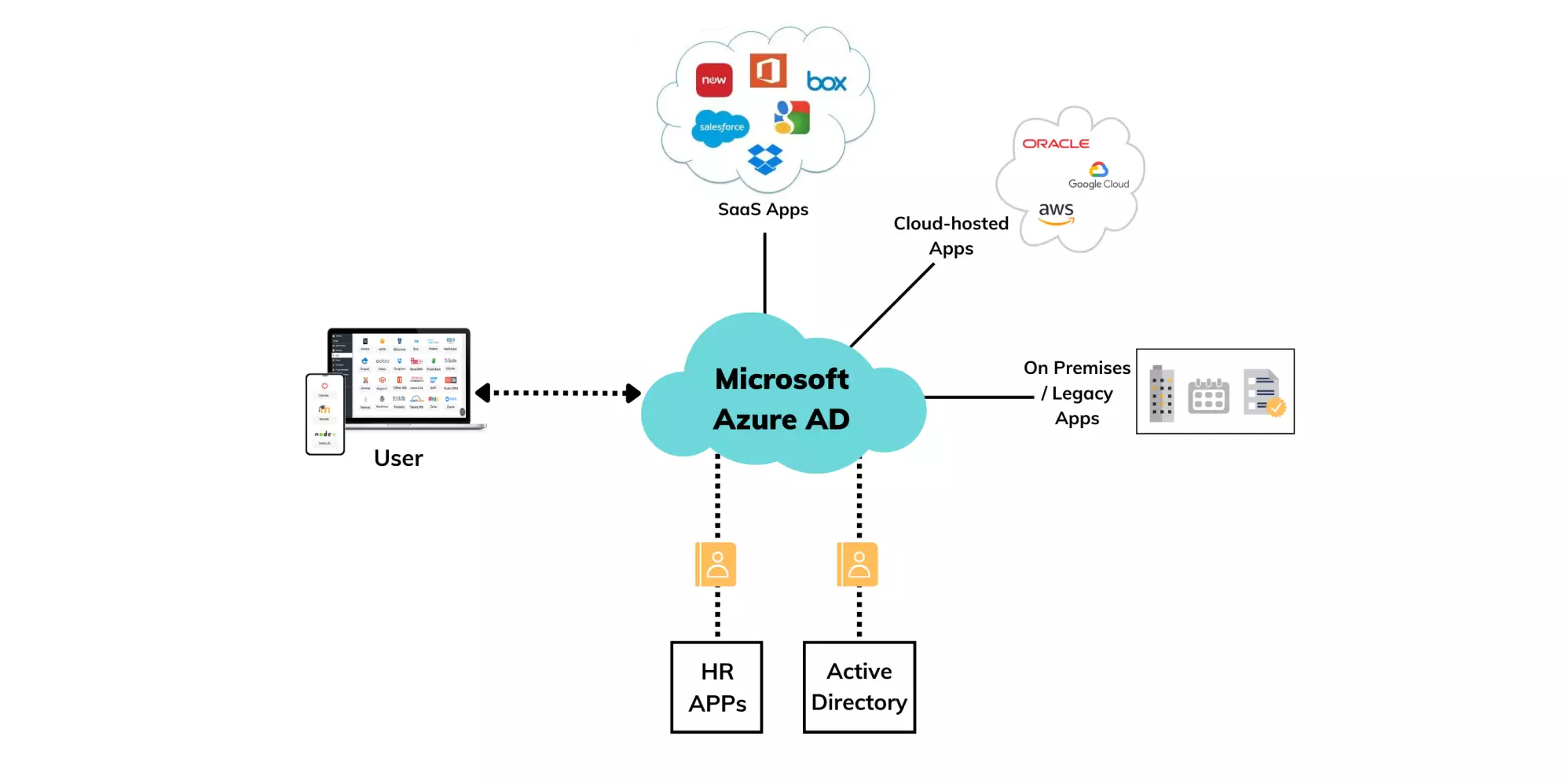
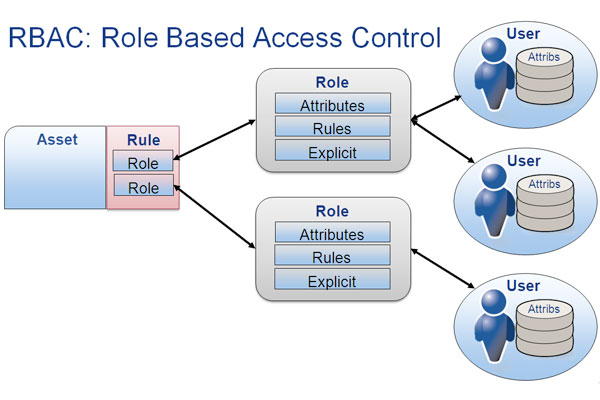
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control is a fundamental aspect of Power BI security. It involves assigning permissions and access rights based on user roles. With RBAC, you can control which users can view, edit, or share specific dashboards, reports, and datasets. This granular level of control ensures that sensitive data is accessible only to those with the appropriate permissions.
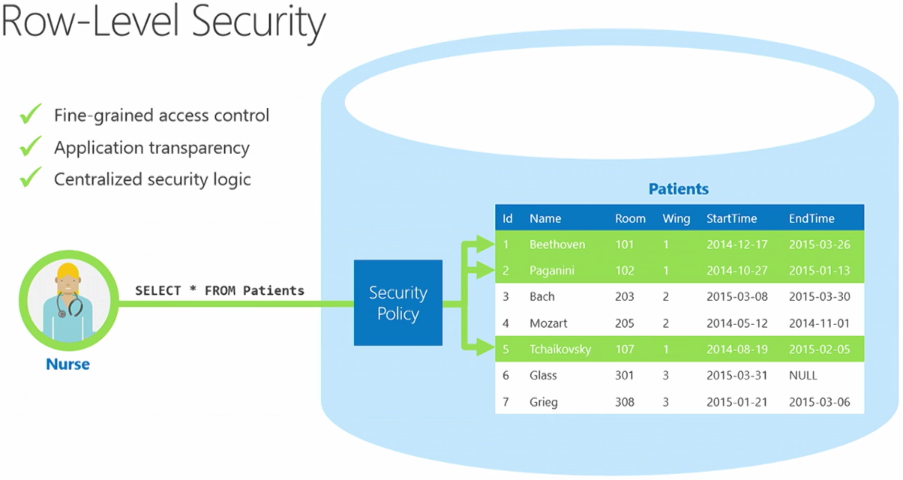
Row-Level Security (RLS)
Row-Level Security is a powerful feature that filters data at the row level, ensuring users can only view data relevant to their role or department. RLS allows you to define rules that restrict data access, providing an additional layer of security. For example, a sales manager can view data for their region, while a VP of Sales can access data for all regions.
Best Practices for Securing Your Data
Now that we understand the security features Power BI offers, let’s explore some best practices to fortify your data security.
Choose the Right Deployment Model
Power BI offers two main deployment models: cloud-based and on-premises. Each model has unique security considerations.
Cloud-based Deployment: When opting for a cloud-based deployment, ensure that you leverage the security features provided by Microsoft. Utilize Azure Active Directory for user authentication and access control. Additionally, take advantage of Microsoft’s advanced data protection features, such as multi-factor authentication and data loss prevention policies.
On-Premises Deployment: For on-premises deployments, ensure that your Power BI Report Server is securely configured and maintained. Follow best practices for server security, including regular updates and patches, firewall configurations, and access control measures.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security to user authentication. When enabled, users are required to provide two or more verification factors, such as a password and a unique code sent to their mobile device. MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.

Maintain a Secure Data Environment
Data security extends beyond Power BI itself. Here are some practices to ensure a secure data environment:
Secure Data Sources: Ensure that data sources connected to Power BI are equally secure. Implement security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits for your data sources.
Data Classification: Classify your data based on sensitivity and criticality. This helps in applying appropriate security controls and access restrictions.
Data Retention Policies: Define clear data retention policies to avoid storing sensitive data longer than necessary, reducing potential risks.
Control Access with RBAC and RLS
As mentioned earlier, RBAC and RLS are powerful tools to restrict data access. Here’s how you can leverage them effectively:
RBAC: Define clear roles and permissions for users and groups. Limit the number of users with administrative privileges to minimize potential risks. Regularly review and update user access rights as roles change within your organization.
RLS: Utilize RLS to restrict data access at a granular level. This ensures that users only see data relevant to their role or department, maintaining data confidentiality and privacy.

Protecting Your Reports and Dashboards
In addition to securing your data, it’s crucial to protect your Power BI reports and dashboards from unauthorized access or misuse. Here are some best practices:
Report and Dashboard Security
Share Securely: When sharing reports and dashboards, use secure sharing options like “Share with specific people” instead of generating public links. This allows you to control exactly who has access.
Limit Download Options: Consider disabling the “Allow live connection” and “Allow downloading” options when sharing reports. This prevents users from downloading data or creating local copies, reducing the risk of unauthorized distribution.
Watermarking: Enable watermarking to add a layer of protection to your reports. Watermarks can include user information, discouraging unauthorized sharing or distribution.
Control Data Export and Printing
Restrict Data Export: Limit the ability to export data from reports and dashboards. This prevents users from saving sensitive data locally or transferring it to unauthorized locations.
Secure Printing: Enable secure printing options, such as requiring a PIN or password to print reports. This ensures that printed reports are not left unattended and maintains data privacy.
Governance and Compliance
An integral part of Power BI security is maintaining governance and compliance with relevant data protection regulations. Here’s how you can ensure compliance:
Data Privacy and Compliance
Data Privacy Policies: Develop and communicate clear data privacy policies to users, outlining their responsibilities and expectations regarding data handling and sharing.
Data Retention and Deletion: Implement data retention policies and regularly review and delete data that is no longer required, adhering to privacy regulations such as GDPR or industry-specific standards.
Data Anonymization: When using Power BI for analytics, consider anonymizing data to protect user privacy. Techniques like data masking or aggregation can be employed to remove personally identifiable information.
Audit and Monitoring
Audit Logs: Enable and regularly review audit logs to track user activities, detect anomalies, and ensure compliance. Audit logs provide valuable insights into data access, sharing, and usage patterns.
Data Flow Monitoring: Monitor data flows within your Power BI environment to identify potential security risks or data leaks. Look for unusual data movement or access patterns.
User Activity Monitoring: Keep a close eye on user activities, especially for users with elevated privileges. Detect and investigate any suspicious activities promptly.
User Training and Awareness
Even the most robust security measures can be undermined by human error or lack of awareness. User training and awareness play a vital role in maintaining Power BI security:
Security Awareness Training
Regular Training: Conduct regular security awareness training sessions for users to educate them about potential risks, phishing attacks, and safe data handling practices.
Phishing Simulation: Run simulated phishing attacks to test user awareness and identify areas for improvement.
Best Practice Guidelines: Develop and distribute easy-to-understand guidelines on using Power BI securely, covering topics like password management, data sharing, and identifying suspicious activities.
Empower Users to Identify Risks
Report Suspicious Activities: Encourage users to report any suspicious activities, emails, or data requests. Establish a clear process for reporting and investigating potential security incidents.
Password Hygiene: Educate users about the importance of strong passwords and the risks of password sharing. Encourage the use of password managers and regular password updates.
Let’s explore a real-world example of how Power BI security measures can be applied to protect sensitive data.
Case Study: Healthcare Organization
Background: A large healthcare organization uses Power BI to analyze patient data and improve care outcomes. The organization handles highly sensitive patient information, including personal health records, and must comply with strict data privacy regulations.
Challenge: The organization needed to ensure that patient data was secure and accessible only to authorized individuals. They also wanted to provide role-based access to different departments, such as doctors, nurses, and administrators, while maintaining data privacy.
Solution: They implemented the following Power BI security measures:
Data Encryption: All data transmitted to and stored in Power BI was encrypted using industry-standard protocols, ensuring data confidentiality.
RBAC and RLS: Role-based access control was utilized to assign specific permissions to user roles. Doctors could access patient data for their patients, while nurses could view only the data relevant to their department. RLS further restricted data access at the row level, ensuring users saw only the information necessary for their roles.
MFA and Password Policies: Multi-factor authentication was enabled for all users, adding an extra layer of security. Strict password policies, including regular changes and complexity requirements, were also implemented.
Data Retention and Anonymization: The organization defined clear data retention policies, deleting data that was no longer required for analysis. They also employed data anonymization techniques to protect patient privacy when using data for research purposes.
Result: With these security measures in place, the healthcare organization successfully secured sensitive patient data. They achieved compliance with data privacy regulations and improved overall data security, ensuring that only authorized individuals could access patient information.
Conclusion
Securing your data and reports in Power BI is essential to protect your organization’s valuable assets and maintain data privacy. By implementing the best practices outlined in this article, you can create a robust security framework that safeguards your information. Remember, data security is an ongoing process that requires regular review and updates. Stay informed about the latest security features and enhancements in Power BI, and adapt your practices accordingly.
As you reflect on the insights provided, what specific aspect of Power BI security do you feel is often overlooked, and how can organizations address this gap to strengthen their overall data security posture? Share your thoughts and insights in the comments below!
