In today’s data-driven business landscape, organizations constantly seek tools to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities. Microsoft’s Power Platform offers two powerful solutions: Power BI and Power Automate. While both tools are part of the same family, they serve distinctly different purposes and solve unique business challenges. This article delves deeply into their functionalities, key differences, features, use cases, integration capabilities, pricing considerations, and best practices for implementation.
The Fundamentals: What Are Power BI and Power Automate?
Power BI Explained
Power BI is Microsoft’s leading business intelligence (BI) and data visualization tool, designed to transform raw data into actionable insights. It enables organizations to create interactive dashboards and comprehensive reports, making data analysis more accessible and efficient. With Power BI, users can analyze sales trends, monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), and generate executive dashboards that provide a clear view of business performance.
One of Power BI’s standout features is its intuitive interface, which caters to users of various technical skill levels. Whether you’re a business decision-maker looking for high-level insights or a data scientist diving deep into analytics, Power BI offers tools that fit your needs. Its drag-and-drop functionality simplifies report creation, allowing users to visualize data effortlessly through a variety of interactive charts and graphs.
Power BI integrates seamlessly with numerous data sources, including cloud services, databases, and spreadsheets. This connectivity ensures that users can pull in real-time data, enabling timely decision-making based on the most current information. Additionally, the platform supports advanced data modeling, allowing users to define relationships between data sets and create calculated measures using Data Analysis Expressions (DAX).
Collaboration is also a key aspect of Power BI. Users can share dashboards and reports through the Power BI Service, facilitating teamwork and ensuring that stakeholders have access to the insights they need. Security features, such as row-level security, protect sensitive data, allowing organizations to control who can view specific information.
Power BI is a versatile and powerful tool that democratizes data analysis, empowering organizations to harness the full potential of their data for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Power Automate Explained
Formerly known as Microsoft Flow, Power Automate is a robust workflow automation platform developed by Microsoft to help organizations streamline repetitive tasks and optimize business processes. By connecting various applications and services, Power Automate empowers users to create seamless automated workflows that enhance efficiency and productivity across diverse organizational functions.
One of the core strengths of Power Automate lies in its ability to automate a wide range of tasks, from simple processes like sending email notifications to more complex multi-step approval workflows. Users can set triggers based on specific events, such as receiving an email or updating a file, which then initiate the corresponding actions automatically. This capability minimizes manual effort, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities rather than routine tasks.
The platform features an intuitive, user-friendly interface that allows users to design workflows visually. With a library of pre-built templates, even those with minimal technical skills can easily implement automation tailored to their needs. Additionally, Power Automate supports over 400 connectors, enabling integration with popular applications like Microsoft 365, SharePoint, Salesforce, and more, facilitating data flow between systems.
Power Automate also incorporates AI capabilities, enabling users to build intelligent workflows that can analyze data and make predictions. For instance, AI Builder allows users to automate tasks like document processing and form recognition, enhancing operational efficiency further.
Collaboration and transparency are enhanced through Power Automate’s shared workflows, which can be accessed and monitored by team members. This fosters a culture of accountability and allows for better tracking of task progress and performance metrics.
Power Automate is an essential tool for organizations looking to automate processes, reduce manual workload, and improve overall productivity, making it a vital component of the modern business landscape.
Key Differences Between Power BI and Power Automate
Primary Purpose
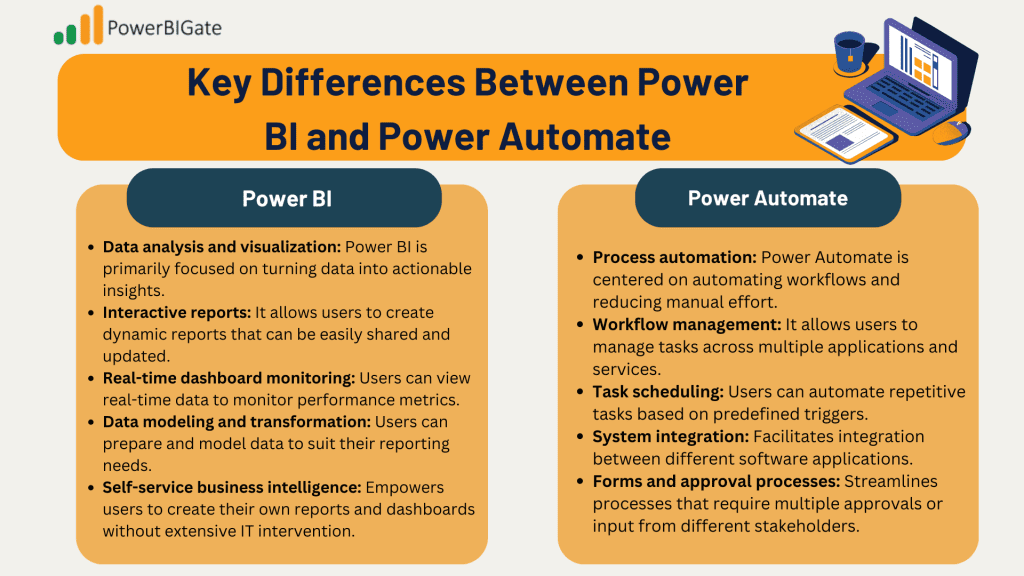
Power BI:
- Data analysis and visualization: Power BI is primarily focused on turning data into actionable insights.
- Interactive reports: It allows users to create dynamic reports that can be easily shared and updated.
- Real-time dashboard monitoring: Users can view real-time data to monitor performance metrics.
- Data modeling and transformation: Users can prepare and model data to suit their reporting needs.
- Self-service business intelligence: Empowers users to create their own reports and dashboards without extensive IT intervention.
Power Automate:
- Process automation: Power Automate is centered on automating workflows and reducing manual effort.
- Workflow management: It allows users to manage tasks across multiple applications and services.
- Task scheduling: Users can automate repetitive tasks based on predefined triggers.
- System integration: Facilitates integration between different software applications.
- Forms and approval processes: Streamlines processes that require multiple approvals or input from different stakeholders.
Target Users
Power BI:
- Data analysts: Those responsible for interpreting data and creating reports.
- Business intelligence professionals: Individuals focused on BI strategies and implementations.
- Report creators: Users who generate reports for various stakeholders.
- Business decision-makers: Executives who rely on data for informed decision-making.
- Data scientists: Professionals who utilize data to derive predictive insights and analytics.
Power Automate:
- Process administrators: Individuals managing workflows and business processes.
- IT professionals: Those responsible for system integrations and automating IT tasks.
- Business users: Employees who benefit from automated processes in their daily tasks.
- Operations managers: Individuals overseeing operational efficiency and process optimization.
- System integrators: Professionals focused on connecting disparate systems for seamless operations.
Feature Comparison: Power BI vs. Power Automate
Power BI’s Standout Features
- Data Visualization:
- Interactive charts and graphs that provide intuitive data representation.
- A custom visuals marketplace where users can find and implement various visualizations.
- A drag-and-drop interface that simplifies report creation.
- Real-time data updates that ensure dashboards reflect the latest information.
- Mobile optimization for access on smartphones and tablets.
- Data Modeling:
- DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) for advanced data calculations and measures.
- Relationship management tools to define how data tables interact.
- Data transformation capabilities to clean and shape data.
- Query editing to manipulate data sources.
- Robust data source connections to various databases and services.
- Sharing and Collaboration:
- Power BI Service for cloud-based report sharing and collaboration.
- Workspace management for organizing reports and dashboards among teams.
- Row-level security to control data visibility based on user roles.
- Report embedding options for integrating BI into other applications.
- Mobile apps for accessing reports on the go.
Power Automate’s Standout Features
- Workflow Creation:
- A visual flow designer that allows users to map out workflows easily.
- A templates library with pre-built flows for common scenarios.
- Trigger management to define what actions initiate workflows.
- Error handling to manage exceptions and ensure process reliability.
- Flow checking to validate workflows before deployment.
- Connectivity:
- Over 400 connectors for popular applications and services.
- Custom connectors for integrating proprietary or less common systems.
- API integration to enable workflows with third-party applications.
- On-premises data gateway for connecting to local data sources.
- Cloud services integration to facilitate cross-platform workflows.
- AI Capabilities:
- AI Builder integration for enhancing workflows with machine learning capabilities.
- Document processing for automating data extraction from documents.
- Form processing to streamline data collection through forms.
- Object detection for identifying and categorizing images.
- Prediction models to forecast outcomes based on historical data.
Use Cases: When to Choose Each Tool
Power BI Best Use Cases
- Financial Analysis:
- Budget tracking and monitoring financial performance.
- Revenue forecasting to predict future sales.
- Expense analysis for cost management.
- Profit margin assessments to evaluate profitability.
- Investment return analysis for assessing financial health.
- Sales and Marketing:
- Sales performance analysis to measure effectiveness.
- Campaign effectiveness tracking to evaluate marketing initiatives.
- Customer analytics to understand buying behavior.
- Market trend analysis for strategic planning.
- Lead conversion metrics to optimize sales processes.
- Operations Management:
- Inventory tracking for supply chain efficiency.
- Supply chain monitoring to identify bottlenecks.
- Production efficiency analysis to improve manufacturing processes.
- Quality control metrics to maintain product standards.
- Resource allocation assessments to optimize resource use.
Power Automate Best Use Cases
- Document Management:
- Automating approval workflows to speed up decision-making.
- Organizing files for better document management.
- Routing documents to the appropriate stakeholders automatically.
- Implementing version control for document updates.
- Managing document archives for compliance and accessibility.
- HR Processes:
- Automating onboarding workflows for new hires.
- Streamlining leave requests and approvals.
- Managing performance reviews with automated reminders.
- Organizing training management workflows.
- Conducting employee surveys for feedback collection.
- Customer Service:
- Automating ticket routing to ensure prompt responses.
- Creating response automation to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Setting follow-up reminders for customer interactions.
- Conducting satisfaction surveys to gauge customer feedback.
- Implementing case management workflows for efficient issue resolution.
Integration Capabilities and Synergies
How They Work Together
While distinct in their primary functions, Power BI and Power Automate can work together to create powerful solutions that enhance organizational efficiency.
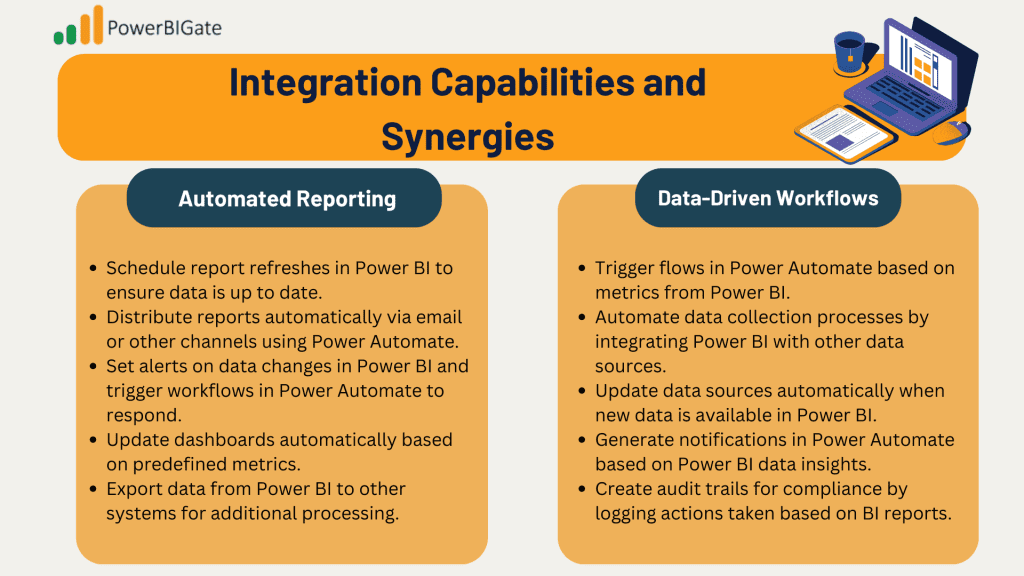
- Automated Reporting:
- Schedule report refreshes in Power BI to ensure data is up to date.
- Distribute reports automatically via email or other channels using Power Automate.
- Set alerts on data changes in Power BI and trigger workflows in Power Automate to respond.
- Update dashboards automatically based on predefined metrics.
- Export data from Power BI to other systems for additional processing.
- Data-Driven Workflows:
- Trigger flows in Power Automate based on metrics from Power BI.
- Automate data collection processes by integrating Power BI with other data sources.
- Update data sources automatically when new data is available in Power BI.
- Generate notifications in Power Automate based on Power BI data insights.
- Create audit trails for compliance by logging actions taken based on BI reports.
Pricing and Licensing Considerations
Power BI Pricing Models
- Power BI Free:
- Basic features suitable for individual use.
- Limited sharing capabilities.
- 1 GB storage for datasets.
- Daily refresh for data sources.
- Power BI Pro:
- Full feature access for collaborative environments.
- Enhanced sharing capabilities among users.
- 10 GB storage for datasets.
- Hourly refresh for data sources.
- Power BI Premium:
- Advanced features for large organizations.
- Dedicated resources for high-demand environments.
- Unlimited storage options.
- Advanced AI capabilities for deeper insights.
Power Automate Pricing Models
- Free with Office 365:
- Basic flows for personal productivity.
- Standard connectors available.
- Limited number of runs per month.
- Per User Plan:
- Unlimited flows for individual users.
- Access to premium connectors and advanced management features.
- AI Builder integration for enhanced automation.
- Per Flow Plan:
- Specific licensing for high-volume flows.
- Organization-wide use for shared workflows.
- Custom pricing based on enterprise needs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Organization
Decision Factors to Consider
- Business Needs:
- Assess data analysis requirements and whether Power BI meets those needs.
- Evaluate process automation needs and how Power Automate can streamline workflows.
- Consider integration requirements with existing systems.
- Gauge user expertise and readiness to adopt new tools.
- Factor in budget constraints for software investments.
- Technical Requirements:
- Identify data sources that will be utilized in Power BI.
- Ensure system compatibility for seamless integration with existing software.
- Review security requirements to protect sensitive data.
- Consider scalability needs as the organization grows.
- Establish performance expectations to ensure smooth operation.
- User Adoption:
- Assess training requirements for users to effectively use the tools.
- Evaluate user familiarity with data analytics and automation concepts.
- Determine support needs for ongoing tool usage.
- Plan for implementation timeframes and resource allocation.
- Address change management to facilitate smooth transitions.
Implementation Best Practices
Power BI Implementation Tips
- Start Small:
- Focus on key metrics and build basic reports to avoid overwhelming users.
- Train key users who can champion the tool and assist others.
- Gather feedback to refine reports and dashboards before scaling up.
- Data Governance:
- Define data standards and best practices for report creation.
- Implement security measures to protect sensitive information.
- Document processes to ensure consistency and compliance.
- Manage access controls to regulate who can view or edit reports.
- Monitor usage to understand how reports are being utilized.
Power Automate Implementation Tips
- Process Analysis:
- Map current workflows to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
- Set clear automation goals to focus efforts effectively.
- Define metrics to measure the success of automated workflows.
- Plan implementation phases to roll out automation gradually.
- Testing and Monitoring:
- Thoroughly test workflows before deploying them to ensure they function correctly.
- Monitor performance regularly to identify areas for improvement.
- Track errors to quickly address any issues that arise.
- Optimize flows based on feedback and performance data.
- Maintain documentation to support ongoing management and troubleshooting.
Future Outlook and Trends
Both Power BI and Power Automate continue to evolve, with Microsoft investing heavily in AI and machine learning. These advancements enhance both platforms, making them more powerful and user-friendly. For example, features such as AI-driven insights in Power BI and advanced AI capabilities in Power Automate are set to redefine how organizations use data and automation.
As organizations strive for greater efficiency, integrating Power BI and Power Automate is likely to become a standard practice. Businesses should stay informed about updates, new features, and industry trends to maximize their investments in these tools. Continuous learning and adaptation will be key to leveraging the full potential of the Power Platform.
Conclusion
Choosing between Power BI and Power Automate isn’t always a straightforward decision; in fact, many organizations find significant value in using both tools together to create comprehensive business solutions. Each tool offers unique strengths that, when combined, can greatly enhance operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities.
Power BI excels in data visualization and analysis, transforming raw data into interactive dashboards and insightful reports. It allows organizations to gain a clear understanding of key performance indicators (KPIs), track sales trends, and make informed business decisions based on real-time data. By presenting information visually, Power BI empowers users across all levels—from data scientists to business executives—to interpret complex datasets easily.
On the other hand, Power Automate focuses on streamlining processes and automating repetitive tasks. It connects various applications and services, enabling organizations to create workflows that eliminate manual efforts. For instance, it can automate approvals, manage notifications, and facilitate data transfers between systems. This not only saves time but also reduces the risk of errors associated with manual processes.
When used together, Power BI and Power Automate can significantly enhance organizational productivity. For example, businesses can set up automated workflows in Power Automate that trigger based on specific data thresholds identified in Power BI dashboards. This synergy allows organizations to react quickly to changing business conditions and drive continuous improvement.
Ultimately, understanding your organization’s specific needs and use cases is crucial in determining how to leverage these tools effectively. By evaluating the requirements for data analysis and process automation, organizations can decide whether to implement Power BI, Power Automate, or both. This strategic approach can maximize value, streamline operations, and support data-driven decision-making across the enterprise.
Discussion Question
We’d love to hear about your experiences with Power BI and Power Automate. Which tool has made a bigger impact on your organization’s efficiency and decision-making processes? Share your success stories, challenges, and tips in the comments below. Have you found innovative ways to use these tools together? Let’s learn from each other’s experiences!
