In the data-driven era, organizations are harnessing the power of advanced analytics and data visualization tools to make informed decisions and drive strategic insights. Microsoft Power BI and Tableau stand out as two of the most prominent and influential tools in the market, each with its own unique features and capabilities.
Revolutionizing the way data is presented and analyzed, Power BI and Tableau have become essential for businesses seeking to extract value from their data. This comprehensive comparison will delve into the key aspects of these tools, including ease of use, pricing models, integration options, and more, helping you determine which one aligns best with your data visualization needs and requirements.
Introduction to Power BI and Tableau
Before delving into the detailed comparison, let’s briefly introduce these two powerful data visualization tools.Microsoft Power BI is a suite of business analytics tools developed by Microsoft. It aims to provide interactive visualizations and business intelligence capabilities, enabling users to easily create dashboards, reports, and insights from various data sources. Power BI offers seamless integration with other Microsoft products and services, making it a popular choice among organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.Tableau is a visual analytics platform that enables users to analyze and visualize data in a flexible and intuitive manner. With a focus on providing powerful yet user-friendly data exploration, Tableau allows users to quickly connect to data sources, create insightful visualizations, and build interactive dashboards. Tableau is known for its extensive customization options and robust data handling capabilities.As we explore the features and benefits of each tool, you will gain a clearer understanding of how Power BI and Tableau can empower your organization to make data-driven decisions and unlock valuable insights.Now, let’s dive into the detailed comparison, keeping in mind the focus keyword “Power BI vs Tableau” and ensuring it is seamlessly integrated into the introduction.


Ease of Use and Learning Curve
Power BI and Tableau both offer user-friendly interfaces and intuitive features that make them accessible to beginners and advanced users alike. However, there are some differences in their learning curves.Power BI has a relatively gentle learning curve, especially for those already familiar with the Microsoft ecosystem. Its drag-and-drop interface and pre-built templates make it easy for beginners to create basic visualizations and dashboards. As users become more proficient, they can explore Power BI’s more advanced features, such as DAX formulas and custom visualizations.Tableau, on the other hand, offers a steeper learning curve. While it also provides a drag-and-drop interface, the vast array of features and customization options can be initially overwhelming for new users. Tableau has a higher ceiling for advanced users, offering intricate control over visualizations and dashboard design. However, this also means that beginners might require more time and resources to become proficient in Tableau.
Data Connectivity and Integration Options
Both Power BI and Tableau offer robust data connectivity, allowing users to connect to a wide range of data sources and import data for analysis.Power BI shines when it comes to integration with other Microsoft products. It seamlessly connects with Excel, SharePoint, and SQL Server, making it a natural choice for organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. Power BI also offers a wide range of connectors to popular data sources such as Google Analytics, Salesforce, and Amazon Redshift.Tableau also offers strong data connectivity, with support for a broad range of data sources including Excel, SQL databases, and cloud-based data warehouses. One area where Tableau excels is in its support for Big Data sources. It offers native connectors to Hadoop, Spark, and cloud data services, making it a powerful tool for analyzing large and complex datasets.
Visualization and Dashboard Capabilities
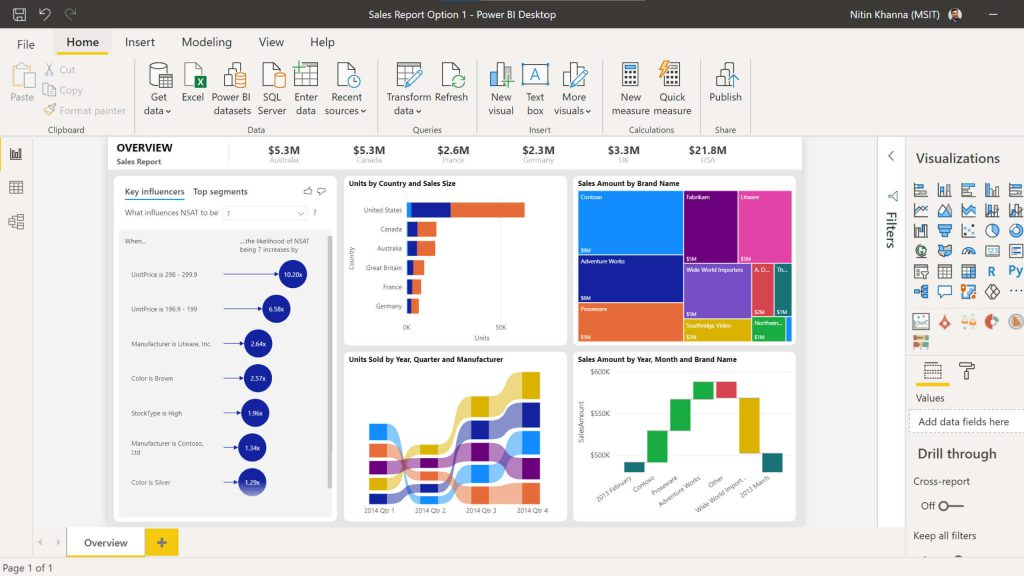
Power BI
Power BI provides a comprehensive set of visualization options to cater to various analytical needs. Here are some key advantages and features:
- Wide Range of Visualization Types: Power BI offers a variety of charts, maps, treemaps, scatter plots, and custom visuals. This diversity allows users to choose the most suitable visualization for their data, making it easier to interpret and understand.
- AI-Powered Insights: Power BI’s built-in AI capabilities can automatically identify trends and patterns, enhancing the analytical process. This feature saves time and provides quick insights, making data exploration more efficient.
- Interactive Dashboards: Power BI dashboards are highly interactive, allowing users to drill down into data, apply cross-filters, and use natural language queries. This interactivity enables users to explore data from different angles and gain deeper insights.
- Bing Maps Integration: Power BI has built-in support for Bing Maps, enabling geographic data visualization. This feature enhances location-based analysis and provides a visual representation of data distributed across different regions or countries.
- Natural Language Queries: Power BI allows users to ask questions about their data using natural language. This feature makes data exploration more accessible and intuitive, as users can simply ask questions and receive visual responses.
- Custom Visuals: Power BI offers a marketplace of custom visuals created by the Power BI community. This extends the range of visualization options and allows users to find unique and specialized chart types.
However, Power BI also has some limitations in terms of visualization capabilities:
- Limited Advanced Customization: While Power BI provides a wide range of visualization types, the level of customization might not be as extensive as Tableau. For users seeking highly customized and intricate visualizations, Power BI may not offer the same level of flexibility.
- Performance with Large Datasets: Power BI might struggle with extremely large datasets, especially when used in the cloud. This could impact the rendering speed and overall performance of visualizations.
- Map Visualization Limitations: While Bing Maps integration is useful, Power BI’s geographic visualization capabilities are not as advanced as Tableau’s. The level of detail and customization options for maps might not meet the needs of organizations with a strong focus on geographic analysis.
Tableau
Tableau is known for its powerful and flexible visualization capabilities, offering a rich set of features:
- Intricate Customization: Tableau provides a high level of flexibility and control over visualization design. It allows users to create unique and intricate visualizations, ensuring dashboards stand out and effectively convey complex information.
- Storytelling Capabilities: Tableau excels in storytelling, allowing users to create narrative-driven dashboards. This feature enhances the communication of insights and makes dashboards more engaging and memorable.
- Advanced Map Visualization: Tableau offers multiple map types, custom territories, and detailed maps for specific regions and countries. This capability is particularly useful for organizations with a strong focus on geographic analysis.
- Big Data Visualization: Tableau has native connectors to Hadoop and Spark, making it ideal for visualizing large and complex datasets. Its ability to handle big data sources ensures organizations can derive insights from vast amounts of information.
- Community and Resources: Tableau has an active user community, providing a wealth of resources, tutorials, and inspiration. Tableau Public showcases user-created visualizations, offering a platform for learning and sharing best practices.
However, there are also a few limitations to consider with Tableau’s visualization capabilities:
- Steep Learning Curve: The vast array of visualization options and customization features in Tableau can be initially overwhelming for new users. It may take more time and resources for users to become proficient in leveraging all that Tableau has to offer.
- Pricing for Advanced Features: Some of Tableau’s most advanced visualization features, such as story points and advanced map types, are available only in the more expensive plans. This could be a consideration for organizations on a tight budget.
- Limited Microsoft Ecosystem Integration: While Tableau does offer connectors to Microsoft products, the level of integration is not as seamless as Power BI. For organizations heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, this could be a drawback.
Pricing and Deployment Options
Power BI offers a freemium model, with a basic version available for free and additional features available through paid plans. The paid plans are priced per user, with the Pro plan starting at $9.99/user/month and the Premium plan priced based on dedicated cloud compute capacity. Power BI can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, providing flexibility for organizations with specific data storage requirements.Tableau also offers a range of pricing plans, including a Creator plan for individuals, an Explorer plan for viewers and ad-hoc authors, and a Viewer plan for read-only users. The Creator plan, comparable to Power BI Pro, starts at $70/user/month. Tableau offers on-premises or cloud deployment options, with additional pricing variations based on the deployment choice.
Support and Community
Both Power BI and Tableau have robust support systems and active user communities.Power BI users can access a wealth of online resources, including Microsoft’s extensive documentation, community forums, and video tutorials. Power BI also offers dedicated support through its website, with options for paid priority support. The Power BI user community is very active, with users sharing insights, custom visuals, and best practices.Tableau also boasts a strong support system, with 24/7 support for all plans, access to an extensive knowledge base, and an active user community. Tableau’s community forums and Tableau Public provide a platform for users to share their work, ask questions, and find inspiration.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Power BI
Advantages:
- Ease of Use: Power BI offers a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to beginners and those familiar with the Microsoft ecosystem. Its drag-and-drop functionality simplifies the creation of basic visualizations and dashboards.
- Seamless Integration: Power BI integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products such as Excel, SharePoint, and SQL Server. This makes it a natural choice for organizations already invested in Microsoft tools, ensuring smooth data flow and reducing the learning curve for users.
- Flexible Pricing: With a freemium model, Power BI provides a cost-effective entry point. The paid plans are priced per user, offering flexibility and scalability. The basic version also includes many features, making it a powerful option even for those on a tight budget.
- AI-Powered Insights: Power BI’s built-in AI capabilities can automatically identify trends and patterns in data. This enhances the analytical process by providing quick insights and saving time for users.
- Interactive Dashboards: Power BI dashboards are highly interactive, allowing users to drill down into data, apply cross-filters, and use natural language queries. This interactivity enhances the exploration and understanding of data.
- Deployment Options: Power BI can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, catering to organizations with specific data storage requirements and providing control over data security.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Advanced Customization: While Power BI offers a wide range of visualization options, it may not provide the same level of intricate customization as Tableau. For users seeking highly customized and unique visualizations, Power BI might fall short.
- Learning Curve for Advanced Features: Although Power BI is easy to get started with, unlocking its more advanced features, like DAX formulas and custom visuals, requires a steeper learning curve. Users seeking to leverage Power BI’s full potential will need additional training and time investment.
- Performance with Large Datasets: Power BI might struggle with extremely large datasets, especially when used in the cloud. For organizations dealing with big data, this could be a significant drawback, requiring additional investments in Power BI’s premium offerings.
- Limited Geographic Visualization: While Power BI offers built-in Bing Maps integration, its geographic visualization capabilities are not as extensive as Tableau’s. For organizations with a strong focus on geographic data analysis, this could be a disadvantage.
Tableau
Advantages:
- Advanced Customization: Tableau offers a high level of flexibility and control over visualization design. It provides intricate customization options, allowing users to create unique and intricate visualizations that stand out.
- Storytelling Capabilities: Tableau excels in its storytelling features, enabling users to create narrative-driven dashboards that guide viewers through data insights. This capability enhances the communication of complex information and makes dashboards more engaging.
- Big Data Connectivity: Tableau has native connectors to Hadoop, Spark, and cloud data services, making it a powerful tool for analyzing large and complex datasets. This strength is particularly advantageous for organizations dealing with big data.
- Map Visualization: Tableau offers multiple map types and custom territories, providing strong geographic visualization capabilities. This includes detailed maps for specific regions and countries, enhancing location-based analysis.
- Community and Resources: Tableau has an active and supportive user community. Tableau Public and the community forums provide a wealth of resources, tutorials, and inspiration for users to learn from and share their work.
Disadvantages:
- Steep Learning Curve: Tableau’s interface, packed with features and options, can be initially overwhelming for new users. The vast array of functionalities may require more time and resources for users to become proficient, especially those new to data visualization.
- Pricing Structure: Tableau’s pricing plans are generally more expensive than Power BI’s, with the Creator plan (comparable to Power BI Pro) starting at $70/user/month. For organizations with a large number of users, the cost can add up quickly.
- Microsoft Ecosystem Integration: While Tableau offers strong connectivity options, its integration with the Microsoft ecosystem is not as seamless as Power BI’s. For organizations heavily reliant on Microsoft tools, this could be a drawback.
- Limited AI Functionality: Unlike Power BI, Tableau lacks built-in AI-powered insights. While Tableau does offer some machine learning capabilities, they are not as extensive or automated as those found in Power BI.
Conclusion
Both Power BI and Tableau are exceptional data visualization tools, each with its own unique strengths and features. Power BI offers a gentle learning curve, seamless integration with Microsoft products, and flexible deployment options. On the other hand, Tableau provides intricate control over visualizations, strong support for Big Data sources, and powerful storytelling capabilities.The choice between Power BI and Tableau ultimately depends on your specific needs and requirements. If you prioritize ease of use, seamless Microsoft integration, and flexible pricing, Power BI might be the better choice. However, if you require advanced customization, intricate visualizations, and strong Big Data capabilities, Tableau could be the preferred option.By considering your organization’s specific requirements, data sources, and user needs, you can make an informed decision between these two powerful data visualization tools.
